Globoid (botany)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
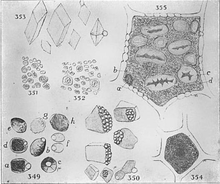
A variety of crystalloids and globoids.
A globoid is a spherical crystalline inclusion in a protein body found in seed tissues that contains phytate and other nutrients for plant growth. These are found in several plants, including wheat and the genus Cucurbita. These nutrients are eventually completely depleted during seedling growth.[1][2] In Cucurbita maxima globoids form as early as the 3rd day of seedling growth.[3] They are located in conjunction with a larger crystalloid.[4] They are electron–dense and vary widely in size.[5]
References
- ↑ Beecroft, Penny; Lott, John N. A. (1996). "Changes in the Element Composition of Globoids From Cucurbita maxima and Cucurbita andreana Cotyledons During Early Seedling Growth". Canadian Journal of Botany 74 (6): 838–847. doi:10.1139/b96-104.
- ↑ Spitzer, Ernest; Webber, Mel; Lott, John N. A. (1981). "Elemental Composition of Globoid Crystals in Protein Bodies of Wheat Grain Grown on Soil Treated with Sewage Sludge". Canadian Journal of Botany 59 (3): 403–409. doi:10.1139/b81-055.
- ↑ Pitt, Michael W.; Lott, John N. A. (1996). "Large Globoid Particles in the Cotyledons of Cucurbita maxima Seedlings". Canadian Journal of Botany 74 (7): 1186–1189. doi:10.1139/b96-141.
- ↑ Pollock, James Barkley (1922). Laboratory Directions for Elementary Botany. Ann Arbor, MI: George Wahr Publishing. p. 29.
- ↑ Lott, John N. A. (2008). "Protein Bodies in Seeds". Nordic Journal of Botany 1 (3): 421–432. doi:10.1111/j.1756-1051.1981.tb00708.x.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.