Germanium tetrafluoride
| Germanium tetrafluoride | |
|---|---|
 | |
| IUPAC name Germanium tetrafluoride | |
| Other names Germanium(IV) fluoride | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 7783-58-6 |
| PubChem | 82215 |
| ChemSpider | 11282354 |
| EC number | 232-011-3 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:[Ge+4].[F-].[F-].[F-].[F-]|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties[1] | |
| Molecular formula | GeF4 |
| Molar mass | 148.634 g/mol |
| Appearance | colourless gas |
| Density | 6.074 g/L (gas), 2.46 g/mL (liquid)[2] |
| Melting point | −15 °C; 5 °F; 258 K (at 4 bar) |
| Boiling point | −36.5 °C; −33.7 °F; 236.7 K (sublimates) |
| Structure | |
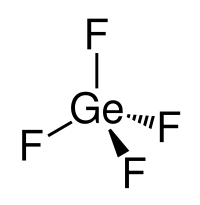
| Molecular shape | tetrahedral |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std enthalpy of formation ΔfH |
-8.008 kJ/g |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases | R26 R35 |
| S-phrases | S9 S26 S28 S36 S45 |
| Main hazards | Reacts with water to form HF, corrosive |
| NFPA 704 |
 0
3
2
|
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Germanium tetrachloride Germanium tetrabromide Germanium tetraiodide |
| Other cations | Carbon tetrafluoride Silicon tetrafluoride Tin tetrafluoride Lead tetrafluoride |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Germanium tetrafluoride (GeF4) is a chemical compound of germanium and fluorine. This colorless gas is formed by reacting germanium with fluorine or germanium dioxide (GeO2) with hydrofluoric acid (HF). Germanium difluoride can be synthesized by reacting germanium tetrafluoride with powdered germanium at 150–300 °C.[3]
Synthesis
Germanium tetrafluoride can be prepared by reaction of germanium with fluorine or hydrogen fluoride:
- Ge + 2 F2 → GeF4
It is also formed during the thermal decomposition of a complex salt, Ba[GeF6]:[4]
- Ba(GeF6) → GeF4 + BaF2
Properties
Germanium tetrafluoride is a noncombustible, strongly fuming gas with a garlic odor. It reacts with water to form hydrofluoric acid and germanium dioxide. Molecular decomposition occurs at temperatures above 1000 °C.[5]
Uses
In combination with disilane, germanium tetrafluoride is used for in the synthesis of SiGe.[2]
References
- ↑ Lide, D. R., ed. (2005). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (86th ed.). Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press. p. 4.64. ISBN 0-8493-0486-5.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Germanium(IV) fluoride. sigmaaldrich.com
- ↑ Greenwood, N. N.; Earnshaw, A. (1998). Chemistry of the Elements (second edition). Butterworth Heinemann. pp. 376–377. ISBN 0-7506-3365-4.
- ↑ Georg Brauer: Handbuch der Präparativen Anorganischen Chemie
- ↑ Germaniumtetrafluorid. IFA Database
| ||||||||