Gentiobiose
| Gentiobiose[1] | |
|---|---|
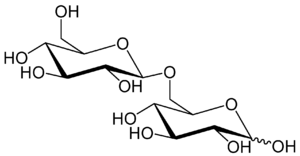 | |
| IUPAC name 6-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-D-glucose | |
| Other names amygdalose | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 554-91-6 |
| PubChem | 441422 |
| ChemSpider | 390156 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:O(C[C@H]1O[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O)[C@@H]2O[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)CO|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C12H22O11 |
| Molar mass | 342.30 g/mol |
| Density | 1.768 g/mL |
| Melting point | 190 to 195 °C; 374 to 383 °F; 463 to 468 K |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Gentiobiose is a disaccharide composed of two units of D-glucose joined with a β(1->6) linkage. It is a white crystalline solid that is soluble in water or hot methanol. Gentiobiose is incorporated into the chemical structure of crocin, the chemical compound that gives saffron its color. It is a product of the caramelization of glucose. [2]
References
- ↑ The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals (11th ed.), Merck, 1989, p. 4288, ISBN 091191028X
- ↑ Sugisawa, Hirqshi; Edo, Hiroshi (1966). "The Thermal Degradation of Sugars I. Thermal Polymerization of Glucose". Journal of Food Science 31 (4): 561. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.1966.tb01905.x.