Genioglossus advancement
Genioglossus advancement (GA) also known as Genial Tubercle Advancement (GTA), is a surgical procedure or sleep surgery in which the base of the tongue is pulled forward, usually to increase airway size due to deformity or a sleep breathing disorder. This procedure is frequently performed with either uvulopalatopharyngoplasty or Maxillomandibular advancement surgeries.
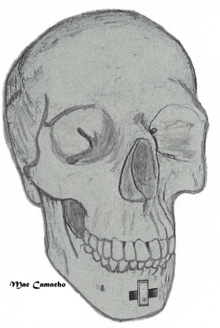
Tongue muscles (genioglossus, geniohyoid and others) are attached to the lower jaw below the teeth. During a genioglossus advancement procedure, a small window or bone cut is made in the front part of the lower jaw (mandible) at the level of the geniotubercle which is where the genioglossus muscle is attached. This piece of bone along with the attachment for the tongue (genial tubercle) is pulled forward and is subsequently secured to the lower jaw, usually with a single screw or with a plate(s) and screws.
This procedure is often combined with other surgeries such as uvulopalatopharyngoplasties or maxillomandibular advancement surgeries. It is rare to have this procedure performed as the only surgical treatment for sleep apnea, as obstruction in sleep apnea is most often at multiple levels (nose, palate, tongue, etc).
 Patient prior to genioglossus advancement, note the narrow airway behind the tongue. |
 Genioglossus advancement, lateral view, after surgery with improved airway behind the tongue. |
 Genioglossus advancement |
 Genioglossus advancement. Note the rectangular bone window, with rotation of the segment of bone. A screw is placed in the lower aspect to hold it in place. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||