Gastrointestinal wall
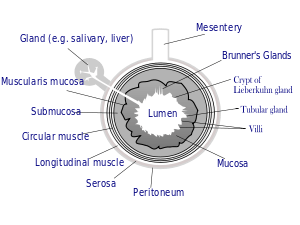
The gastrointestinal wall is a specialised series of layers that surrounds the gastrointestinal tract. The general structure involves four layers, the mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and adventitia or serosa, that may differ slightly in form and function according to the part of the gastrointestinal tract they belong to.
Structure

The gastrointestinal tract has a form of general histology with some differences that reflect the specialization in functional anatomy.
Mucosa
The mucosa is the innermost layer of the gastrointestinal tract. It surrounds the lumen of the tract, and comes into direct contact with digested food (chyme). The mucosa itself is made up of three layers: [1] :264
- The epithelium is the innermost layer. It is where most digestive, absorptive and secretory processes occur.
- Lamina propria is a layer of connective tissue within the mucosa. Unusually cellular compared to most connective tissue
- Muscularis mucosae is a thin layer of smooth muscle.
Epithelium
The mucosae are highly specialized in each organ of the gastrointestinal tract to deal with the different conditions. The most variation is seen in the epithelium: [1]:265
- In the oesophagus, pharynx and external anal canal the epithelium is stratified, squamous and non-keratinising, for protective purposes.
- In the stomach, the epithelium is simple columnar, and is organised into gastric pits and glands to deal with secretion. [1]:265
- In the small intestine, epithelium is simple columnar and specialised for absorption. The epithelium is arranged into villi, creating a brush border and increasing the area for absorption. Each cell also has microvilli. it is organised into plicae circulares and villi, and the enterocytes have microvilli. This creates a brush border which greatly increases the surface area for absorption. The epithelium is simple columnar with microvilli. In the ileum there are occasionally Peyer's patches in the lamina propria. Brunner's glands are found in the duodenum but not in other parts of the small intestine. [1]:265
- In the colon, epithelium is simple columnar and without villi. Goblet cells, which secrete mucous, are also present. [1]:265
- The appendix has a mucosa resembling the colon but is heavily infiltrated with lymphocytes.
Transition between the different types of epithelium occurs at the junction between the oesophagus and stomach; between the stomach and duodenum, between the ileum and caecum, and at the pecinate line of the anus. [1]:264
Submucosa
The submucosa consists of a dense and irregular layer of connective tissue with blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves branching into the mucosa and muscularis externa. It contains Meissner's plexus, an enteric nervous plexus, situated on the inner surface of the muscularis externa. [1]:263
Muscularis externa
The muscularis externa (also known as the muscularis propria[2] ) consists of two layers of muscle, the inner and outer layer. The muscle of the inner layer is arranged in circular rings around the tract, whereas the muscle of the outer layer is arranged longitudinally. The stomach has an extra layer, an inner oblique muscular layer. [1]:263 Between the two muscle layers are the myenteric or Auerbach's plexus. This controls peristalsis. Activity is initiated by the pacemaker cells (interstitial cells of Cajal). The gut has intrinsic peristaltic activity (basal electrical rhythm) due to its self-contained enteric nervous system. The rate can of course be modulated by the rest of the autonomic nervous system.
The layers are not truly longitudinal or circular, rather the layers of muscle are helical with different pitches. The inner circular is helical with a steep pitch and the outer longitudinal is helical with a much shallower pitch.
The coordinated contractions of these layers is called peristalsis and propels the food through the tract. Food in the GI tract is called a bolus (ball of food) from the mouth down to the stomach. After the stomach, the food is partially digested and semi-liquid, and is referred to as chyme. In the large intestine the remaining semi-solid substance is referred to as faeces. The circular muscle layer prevents food from travelling backward and the longitudinal layer shortens the tract.
The thickness of muscularis externa varies in each part of the tract:
- In the colon, for example, the muscularis externa is much thicker because the faeces are large and heavy, and require more force to push along. The outer longitudinal layer of the colon thins out into 3 discontinuous longitudinal bands, known as taeniae coli (bands of the colon). This is one of the 3 features helping to distinguish between the large and small intestine.
- Occasionally in the large intestine (2-3 times a day) there will be mass contraction of certain segments, moving a lot of faeces along. This is generally when one gets the urge to defecate.
- The pylorus of the stomach has a thickened portion of the inner circular layer: the pyloric sphincter. Alone among the GI tract, the stomach has a third layer of muscularis externa. This is the inner oblique layer, and helps churn the chyme in the stomach.
Adventitia/serosa
The outermost layer of the GI tract consists of several layers of connective tissue called the adventitia or serosa (if the tract is within the abdominal cavity). [1]:263
Intraperitoneal parts of the GI tract are covered with serosa. These include most of the stomach, first part of the duodenum, all of the small intestine, caecum and appendix, transverse colon, sigmoid colon and rectum. In these sections of the gut there is clear boundary between the gut and the surrounding tissue. These parts of the tract have a mesentery.
Retroperitoneal parts are covered with adventitia. They blend into the surrounding tissue and are fixed in position. For example, the retroperitoneal section of the duodenum usually passes through the transpyloric plane. These include the esophagus, pylorus of the stomach, distal duodenum, ascending colon, descending colon and anal canal. In addition, the oral cavity has adventitia.
Clinical relevance
Inflammatory bowel disease affects the layers of the gastrointestinal tract in different ways. Ulcerative colitis involves the colonic mucosa. Crohn's disease may produce inflammation in all layers in any part of the gastrointestinal tract and so can result in transmural fistulae.
A perforated ulcer is one that has eroded through the layers of the gastrointestinal tract.
Invasion of tumours through the layers of the gastrointestinal wall is used in staging of tumour spread. This is associated with prognosis.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 Deakin, Barbara Young ... [et al.] ; drawings by Philip J. (2006). Wheater's functional histology : a text and colour atlas (5th ed. ed.). [Edinburgh?]: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-4430-6-8508.
- ↑ "Oral: Four layers of the G.I. tract". The Histology Guide. University of Leeds. Retrieved 4 January 2014.