GNAI1
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i), alpha-1 subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNAI1 gene.[1][2]
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles. [§ 1]
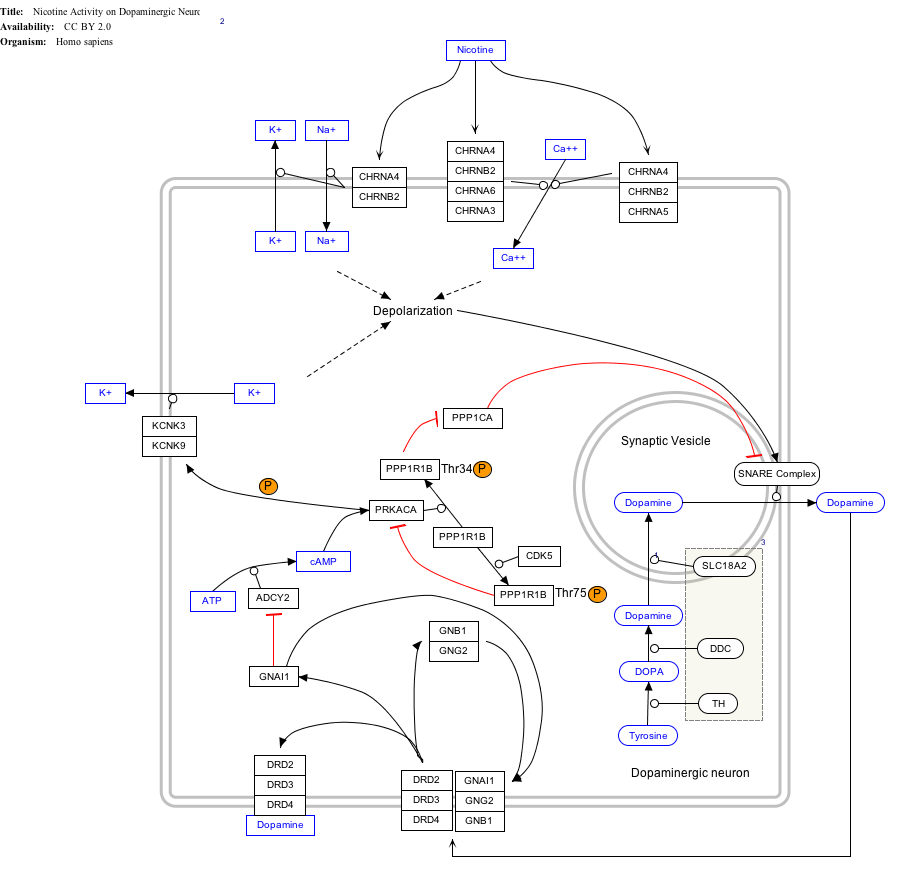
Nicotine Activity on Dopaminergic Neurons edit
- ↑ The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "NicotineDopaminergic_WP1602".
Interactions
GNAI1 has been shown to interact with GPR143,[3] RGS14,[4][5] RIC8A,[6] S1PR1,[7] RGS12[4] and RGS19.[8][9]
References
- ↑ Bray P, Carter A, Guo V, Puckett C, Kamholz J, Spiegel A, Nirenberg M (August 1987). "Human cDNA clones for an alpha subunit of Gi signal-transduction protein". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84 (15): 5115–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.15.5115. PMC 298804. PMID 3110783.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: GNAI1 Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), alpha inhibiting activity polypeptide 1".
- ↑ Schiaffino, M V; d'Addio M, Alloni A, Baschirotto C, Valetti C, Cortese K, Puri C, Bassi M T, Colla C, De Luca M, Tacchetti C, Ballabio A (September 1999). "Ocular albinism: evidence for a defect in an intracellular signal transduction system". Nat. Genet. (UNITED STATES) 23 (1): 108–12. doi:10.1038/12715. ISSN 1061-4036. PMID 10471510.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Kimple, R J; De Vries L, Tronchère H, Behe C I, Morris R A, Gist Farquhar M, Siderovski D P (August 2001). "RGS12 and RGS14 GoLoco motifs are G alpha(i) interaction sites with guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor Activity". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 276 (31): 29275–81. doi:10.1074/jbc.M103208200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 11387333.
- ↑ Kimple, Randall J; Kimple Michelle E, Betts Laurie, Sondek John, Siderovski David P (April 2002). "Structural determinants for GoLoco-induced inhibition of nucleotide release by Galpha subunits". Nature (England) 416 (6883): 878–81. doi:10.1038/416878a. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 11976690.
- ↑ Tall, Gregory G; Krumins Andrejs M, Gilman Alfred G (March 2003). "Mammalian Ric-8A (synembryn) is a heterotrimeric Galpha protein guanine nucleotide exchange factor". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 278 (10): 8356–62. doi:10.1074/jbc.M211862200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 12509430.
- ↑ Lee, M J; Evans M, Hla T (May 1996). "The inducible G protein-coupled receptor edg-1 signals via the G(i)/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 271 (19): 11272–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.19.11272. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 8626678.
- ↑ Woulfe, D S; Stadel J M (June 1999). "Structural basis for the selectivity of the RGS protein, GAIP, for Galphai family members. Identification of a single amino acid determinant for selective interaction of Galphai subunits with GAIP". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 274 (25): 17718–24. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.25.17718. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 10364213.
- ↑ De Vries, L; Elenko E, Hubler L, Jones T L, Farquhar M G (December 1996). "GAIP is membrane-anchored by palmitoylation and interacts with the activated (GTP-bound) form of Gαi subunits". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (UNITED STATES) 93 (26): 15203–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.26.15203. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 26381. PMID 8986788.
Further reading
- Sidhu A, Niznik HB (2000). "Coupling of dopamine receptor subtypes to multiple and diverse G proteins". Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 18 (7): 669–77. doi:10.1016/S0736-5748(00)00033-2. PMID 10978845.
- Brown EJ, Frazier WA (2001). "Integrin-associated protein (CD47) and its ligands". Trends Cell Biol. 11 (3): 130–5. doi:10.1016/S0962-8924(00)01906-1. PMID 11306274.
- Raymond JR, Mukhin YV, Gelasco A et al. (2002). "Multiplicity of mechanisms of serotonin receptor signal transduction". Pharmacol. Ther. 92 (2–3): 179–212. doi:10.1016/S0163-7258(01)00169-3. PMID 11916537.
- Jiang M, Pandey S, Tran VT, Fong HK (1991). "Guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins in retinal pigment epithelial cells". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88 (9): 3907–11. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.9.3907. PMC 51562. PMID 1902575.
- Gennity JM, Siess W (1991). "Thrombin inhibits the pertussis-toxin-dependent ADP-ribosylation of a novel soluble Gi-protein in human platelets". Biochem. J. 279 (Pt 3): 643–50. PMC 1151493. PMID 1953657.
- Itoh H, Toyama R, Kozasa T et al. (1988). "Presence of three distinct molecular species of Gi protein alpha subunit. Structure of rat cDNAs and human genomic DNAs". J. Biol. Chem. 263 (14): 6656–64. PMID 2834384.
- Bloch DB, Bloch KD, Iannuzzi M et al. (1988). "The gene for the alpha i1 subunit of human guanine nucleotide binding protein maps near the cystic fibrosis locus". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 42 (6): 884–8. PMC 1715192. PMID 3130752.
- Nagata K, Katada T, Tohkin M et al. (1988). "GTP-binding proteins in human platelet membranes serving as the specific substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin". FEBS Lett. 237 (1–2): 113–7. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(88)80182-0. PMID 3139448.
- Kagimoto S, Yamada Y, Kubota A et al. (1994). "Human somatostatin receptor, SSTR2, is coupled to adenylyl cyclase in the presence of Gi alpha 1 protein". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 202 (2): 1188–95. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1994.2054. PMID 7914078.
- Nitta K, Uchida K, Kawashima A et al. (1994). "Identification of GTP-binding proteins in human glomeruli". Nippon Jinzo Gakkai shi 36 (1): 9–12. PMID 8107314.
- Law SF, Zaina S, Sweet R et al. (1994). "Gi alpha 1 selectively couples somatostatin receptor subtype 3 to adenylyl cyclase: identification of the functional domains of this alpha subunit necessary for mediating the inhibition by somatostatin of cAMP formation". Mol. Pharmacol. 45 (4): 587–90. PMID 8183236.
- Europe-Finner GN, Phaneuf S, Watson SP, López Bernal A (1993). "Identification and expression of G-proteins in human myometrium: up-regulation of G alpha s in pregnancy". Endocrinology 132 (6): 2484–90. doi:10.1210/en.132.6.2484. PMID 8504751.
- Laugwitz KL, Allgeier A, Offermanns S et al. (1996). "The human thyrotropin receptor: a heptahelical receptor capable of stimulating members of all four G protein families". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93 (1): 116–20. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.1.116. PMC 40189. PMID 8552586.
- Andersson B, Wentland MA, Ricafrente JY et al. (1996). "A "double adaptor" method for improved shotgun library construction". Anal. Biochem. 236 (1): 107–13. doi:10.1006/abio.1996.0138. PMID 8619474.
- Lee MJ, Evans M, Hla T (1996). "The inducible G protein-coupled receptor edg-1 signals via the G(i)/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (19): 11272–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.19.11272. PMID 8626678.
- De Vries L, Elenko E, Hubler L et al. (1997). "GAIP is membrane-anchored by palmitoylation and interacts with the activated (GTP-bound) form of Gαi subunits". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93 (26): 15203–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.26.15203. PMC 26381. PMID 8986788.
- Yu W, Andersson B, Worley KC et al. (1997). "Large-Scale Concatenation cDNA Sequencing". Genome Res. 7 (4): 353–8. doi:10.1101/gr.7.4.353. PMC 139146. PMID 9110174.
- Popov S, Yu K, Kozasa T, Wilkie TM (1997). "The regulators of G protein signaling (RGS) domains of RGS4, RGS10, and GAIP retain GTPase activating protein activity in vitro". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94 (14): 7216–20. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.14.7216. PMC 23796. PMID 9207071.
- Shuey DJ, Betty M, Jones PG et al. (1998). "RGS7 attenuates signal transduction through the G(alpha q) family of heterotrimeric G proteins in mammalian cells". J. Neurochem. 70 (5): 1964–72. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.70051964.x. PMID 9572280.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.