Frontal bone
| Frontal bone | |
|---|---|
 | |
| 19th Century skull showing sword-blade trauma on frontal bone. | |
 | |
| Position of the frontal bone (highlighted in green). | |
| Latin | Os frontale |
| Gray's | p.135 |
| Articulations | Twelve bones: the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the two parietals, the two nasals, the two maxillæ, the two lacrimals, and the two zygomatics |
| MeSH | Frontal+Bone |
| TA | A02.1.03.001 |
| FMA | FMA:52734 |
The frontal bone or os frontis is a bone in the human skull. The name comes from the Latin word frons (meaning "forehead"). The bone resembles a cockleshell in form, and consists of three portions:[1]
- a large vertical portion, the squama frontalis, corresponding with the region of the forehead.
- an orbital or horizontal portion, the pars orbitalis, which enters into the formation of the roofs of the orbital and nasal cavities.
- a nasal portion, it articulates with the nasal bones and the frontal process of the maxilla to form the root of the nose.
Structure
Borders
The border of the squama frontalis is thick, strongly serrated, bevelled at the expense of the inner table above, where it rests upon the parietal bones, and at the expense of the outer table on either side, where it receives the lateral pressure of those bones; this border is continued below into a triangular, rough surface, which articulates with the great wing of the sphenoid. The posterior borders of the orbital plates are thin and serrated, and articulate with the small wings of the sphenoid. [1]
-

Coronal suture separates frontal bone and parietal bones.
-

Sphenofrontal suture separates frontal bone and sphenoid bone.
-

Zygomaticofrontal suture separates frontal bone and zygomatic bones.
-

Nasofrontal suture separates frontal bone and nasal bone.
-

Frontomaxillary suture separates frontal bone and maxilla.
Development
The frontal bone is presumed to be derived from neural crest cells.[2]

The frontal bone is ossified in membrane from two primary centers, one for each half, which appear toward the end of the second month of fetal life, one above each supraorbital margin. From each of these centers, ossification extends upward to form the corresponding half of the squama, and backward to form the orbital plate. The spine is ossified from a pair of secondary centers, on either side of the middle line; similar centers appear in the nasal part and zygomatic processes.
At birth the bone consists of two pieces, separated by the frontal suture, which is usually obliterated, except at its lower part, by the eighth year, but occasionally persists throughout life. It is generally maintained that the development of the frontal sinuses begins at the end of the first or beginning of the second year, but may begins at birth. The sinuses are of considerable size by the seventh or eighth year, but do not attain their full proportions until after puberty.
In other animals
In most vertebrates, the frontal bone is paired, rather than presenting the single, fused structure found in humans (see frontal suture). It typically lies on the upper part of the head, between the eyes, but in many non-mammalian animals it does not form part of the orbital cavity. Instead, in reptiles, bony fish and amphibians it is often separated from the orbits by one or two additional bones not found in mammals. These bones, the prefrontals and postfrontals, together form the upper margin of the eye sockets, and lie to either side of the frontal bones.[3]
In dinosaurs
The frontal bone is one of the principal paired mid-line bones in dinosaur skulls. This bone is part of the skull roof, which is a set of bones that cover the brain, eyes and nostrils. The frontal makes contact with several other bones in the skull. The anterior part of the bone articulates with the nasal bone and the prefrontal bone. The posterior part of the bone articulates with the postorbital bone and the parietal bone. This bone defines all of part of the upper margin of the orbit.
Additional Images
-

Position of the frontal bone (highlighted in green). Animation.
-

Frontal bone (highlighted in green).
-

Frontal bone at the top.
-

Frontal bone (highlighted in green).
-

Skull showing keyhole gunshot trauma on frontal bone, at Civil War (1861-1865).
-

Exploded skull. Frontal bone is at the center top.
-

Frontal bone. Outer surface.
-
Frontal bone at newborn.
-

Frontal bone at birth.
-

Inner surface of the frontal bone (highlighted in green). Parietal bones are removed.
-

Inner surface of the frontal bone (highlighted in green). Parietal bones are removed.
-

Inner surface of the frontal bone (highlighted in red).
-
Frontal bone orbital part at newborn.
-
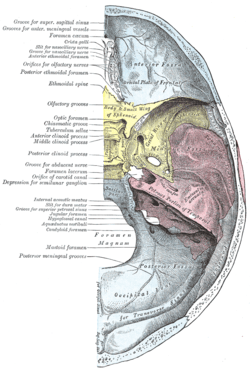
Inner surface of the frontal bone (highlighted in blue at the top).
-

Outer and inner surface of frontal bone. Animation.
-

Sagittal section of skull. Frontal bone is highlighted in blue, at center left.
-

Frontal bone. Inferior surface.
-
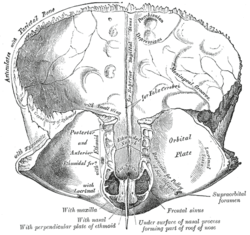
Frontal bone. Inferior surface.
-
Cephalic extremity.Original mummification.
-
Cephalic extremity.Original mummification.
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Frontal bones. |
This article uses anatomical terminology; for an overview, see anatomical terminology.
- Ossification of frontal bone
- Frontal eminence
- Forehead
- Frontal lobe
References
This article incorporates text from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy.
External links
- 23:os-0101 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator, at Elsevier 34256.000-1
| |||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||




