Fried parameter
The Fried parameter[1] or Fried's coherence length (commonly designated as 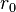 ) is a measure of the quality of optical transmission through the atmosphere due to random inhomogeneities in its refractive index. In practice, such inhomogeneities are primarily due to tiny variations in temperature (and thus density) on smaller spatial scales resulting from random turbulent mixing of larger temperature variations on larger spatial scales as first described by Kolmogorov. The Fried parameter has units of length and is typically expressed in centimeters. It is defined as the diameter of a circular area over which the rms wavefront aberration due to passage through the atmosphere is equal to 1 radian. As such, imaging from telescopes with apertures much smaller than
) is a measure of the quality of optical transmission through the atmosphere due to random inhomogeneities in its refractive index. In practice, such inhomogeneities are primarily due to tiny variations in temperature (and thus density) on smaller spatial scales resulting from random turbulent mixing of larger temperature variations on larger spatial scales as first described by Kolmogorov. The Fried parameter has units of length and is typically expressed in centimeters. It is defined as the diameter of a circular area over which the rms wavefront aberration due to passage through the atmosphere is equal to 1 radian. As such, imaging from telescopes with apertures much smaller than 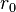 is less affected by atmospheric seeing than diffraction due to the telescope's small aperture. However the imaging resolution of telescopes with apertures much larger than
is less affected by atmospheric seeing than diffraction due to the telescope's small aperture. However the imaging resolution of telescopes with apertures much larger than 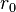 (thus including all professional telescopes) will be limited by the turbulent atmosphere, preventing the instrument from approaching the diffraction limit.
(thus including all professional telescopes) will be limited by the turbulent atmosphere, preventing the instrument from approaching the diffraction limit.
Although not explicitly written in his article, the Fried parameter at wavelength 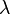 can be expressed[2] in terms of the so-called atmospheric turbulence strength
can be expressed[2] in terms of the so-called atmospheric turbulence strength  (which is actually a function of temperature fluctuations as well as turbulence) along
(which is actually a function of temperature fluctuations as well as turbulence) along  the path of the starlight :
the path of the starlight :
![r_{0}=\left[0.423\,k^{2}\,\int _{{{\mathrm {Path}}}}C_{n}^{2}(z')\,dz'\right]^{{-3/5}}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/7/7/9/b/779b83ba29368acf54c572a98a525a6c.png)
where 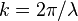 is the wavenumber. If not specified, a reference to the Fried Parameter in astronomy is understood to refer to a path in the vertical direction. When observing at a zenith angle
is the wavenumber. If not specified, a reference to the Fried Parameter in astronomy is understood to refer to a path in the vertical direction. When observing at a zenith angle  , the line of sight passes through an air column which is
, the line of sight passes through an air column which is  times longer, producing a greater disturbance in the wavefront quality. This results in a smaller
times longer, producing a greater disturbance in the wavefront quality. This results in a smaller 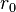 , so that in terms of the vertical path z the operative Fried parameter
, so that in terms of the vertical path z the operative Fried parameter 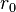 is reduced according to:
is reduced according to:
![r_{0}=\left[0.423\,k^{2}\,\sec \zeta \int _{{{\mathrm {Vertical}}}}C_{n}^{2}(z)\,dz\right]^{{-3/5}}=(\cos \zeta )^{{3/5}}\ r_{0}^{{(vertical)}}.](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/8/f/1/c/8f1ca7a093d2b42899cc51dd86398953.png)
At locations selected for observatories, typical values for 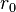 range from 10 cm for average seeing to 20 cm under excellent seeing conditions. The angular resolution is then limited to about
range from 10 cm for average seeing to 20 cm under excellent seeing conditions. The angular resolution is then limited to about 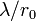 due to the effect of the atmosphere, whereas the resolution due to diffraction by a circular aperture of diameter
due to the effect of the atmosphere, whereas the resolution due to diffraction by a circular aperture of diameter  is generally given as
is generally given as  . Since professional telescopes have diameters
. Since professional telescopes have diameters 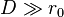 , they can only obtain an image resolution approaching their diffraction limits by employing adaptive optics.
, they can only obtain an image resolution approaching their diffraction limits by employing adaptive optics.
Because 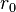 is a function of wavelength, varying as
is a function of wavelength, varying as 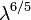 , its value is only meaningful in relation to a specified wavelength. When not stated explicitely, the wavelength is typically understood to be
, its value is only meaningful in relation to a specified wavelength. When not stated explicitely, the wavelength is typically understood to be  .
.
See also
References
- ↑ Fried, D. L. (October 1966). "Optical Resolution Through a Randomly Inhomogeneous Medium for Very Long and Very Short Exposures". Journal of the Optical Society of America 56 (10): 1372–1379. Bibcode:1966JOSA...56.1372F. doi:10.1364/JOSA.56.001372.
- ↑ Hardy, Johw W. (1998). Adaptive optics for astronomical telescopes. Oxford University Press. p. 92. ISBN 0-19-509019-5.