Fraunhofer distance
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Fraunhofer distance, named after Joseph von Fraunhofer, is the value of:
where D is the largest dimension of the radiator (or the diameter of the antenna) and 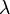 is the wavelength of the radio wave. This distance provides the limit between the near and far field.
is the wavelength of the radio wave. This distance provides the limit between the near and far field.
See also
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.
