Foramen lacerum
| Foramen lacerum | |
|---|---|
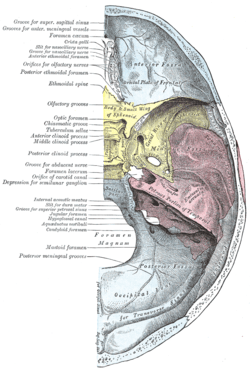 | |
| Base of the skull. Upper surface. (Foramen lacerum is labeled at center left, and is visible as the large hole between yellow sphenoid, red temporal, and blue occipital) | |
| Latin | Foramen lacerum |
| Gray's | subject #47 192 |
The foramen lacerum (Latin for lacerated piercing) is a triangular hole in the base of the skull located between the sphenoid, apex of petrous temporal and basilar part of occipital.
Structure
The foramen lacerum is a foramen situated directly inferior to the opening of the carotid canal. [1]:776
Development
The foramen lacerum fills with cartilage after birth. [1]:776
Function
The internal carotid artery passes from the carotid canal in the base of the skull, emerging and coursing superior to foramen lacerum as it exits the carotid canal. The internal carotid artery does not travel through foramen lacerum. The segment of the internal carotid artery that travels above foramen lacerum is called the lacerum segment. The artery of pterygoid canal, the nerve of pterygoid canal and some venous drainage pass through the foramen lacerum.
- The greater petrosal nerve transits into the foramen lacerum before joining with the nerve of pterygoid canal, which is composed of the deep petrosal nerve and the greater petrosal nerve, the former carrying sympathetic fibres and the latter parasympathetic fibres of the autonomic nervous system to blood vessels, mucous membranes, salivary glands, and lacrimal glands.
- Furthermore, one of the terminal branches of the ascending pharyngeal artery (itself a branch of the external carotid artery) passes through the foramen lacerum. The ascending pharyngeal artery is one of three possible "meningeal branches" of this vessel.
- Some emissary veins pass through the foramen lacerum. These connect the extracranial pterygoid plexus with the intracranial cavernous sinus and present an unopposed route for infection.
- This is also a route for nasopharyngeal carcinoma to gain access to the cavernous sinus and affect cranial nerves. [2]
Clinical relevance
History
Additional images
-

Foramen lacerum
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell ; illustrations by Richard; Richardson, Paul (2005). Gray's anatomy for students. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-8089-2306-0.
- ↑ Christodouleas, Boris Hristov, Steven H. Lin, John P. (2010). Radiation oncology : a question-based review. Philadelphia, Pa.: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 138. ISBN 1608314448.
External links
- SUNY Figs 22:5b-10 - "Internal view of skull."
- Photo of model at Waynesburg College skeleton/foramenlacerum
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (VII)
- Tauber M, van Loveren H, Jallo G, Romano A, Keller J (1999). "The enigmatic foramen lacerum". Neurosurgery 44 (2): 386–91; discussion 391–3. doi:10.1097/00006123-199902000-00083. PMID 9932893.
- Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator, at Elsevier 34257.000-1
- Image at ucsd.edu
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||