Folic acid
| Folic acid | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
 | |
 | |
| IUPAC name (2S)-2-[(4-{[(2-amino-4-hydroxypteridin-6-yl)methyl]amino}phenyl)formamido]pentanedioic acid | |
| Other names N-(4-{[(2-amino-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropteridin-6-yl)methyl]amino}benzoyl)-L-glutamic acid; pteroyl-L-glutamic acid; Vitamin B9; Vitamin Bc; Folacin | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 59-30-3 |
| PubChem | 6037 |
| ChemSpider | 5815 |
| UNII | 935E97BOY8 |
| DrugBank | DB00158 |
| KEGG | C00504 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:27470 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1622 |
| RTECS number | LP5425000 |
| ATC code | B03 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:O=C(N[C@H](C(O)=O)CCC(O)=O)C1=CC=C(NCC2=NC(C(NC(N)=N3)=O)=C3N=C2)C=C1|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C19H19N7O6 |
| Molar mass | 441.40 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow-orange crystalline powder |
| Melting point | 250 °C (523 K) (decomposition) [1] |
| Solubility in water | 1.6 mg/L (25 °C)[1] |
| log P | -2.5 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 1st: 4.65, 2nd: 6.75, 3rd: 9.00[2] |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 |
 0
1
0
|
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Folic acid (also known as vitamin M, vitamin B9,[3] vitamin Bc[4] (or folacin), pteroyl-L-glutamic acid, and pteroyl-L-glutamate) is a form of the water-soluble vitamin B9.[citation needed] Folate is a naturally occurring form of the vitamin, found in food, while folic acid is synthetically produced, and used in fortified foods and supplements.[5] Folic acid is itself not biologically active, but its biological importance is due to tetrahydrofolate and other derivatives after its conversion to dihydrofolic acid in the liver.[6]
Vitamin B9 (folic acid and folate) is essential for numerous bodily functions. Humans cannot synthesize folate de novo; therefore, folate has to be supplied through the diet to meet their daily requirements. The human body needs folate to synthesize DNA, repair DNA, and methylate DNA as well as to act as a cofactor in certain biological reactions.[7] It is especially important in aiding rapid cell division and growth, such as in infancy and pregnancy. Children and adults both require folic acid to produce healthy red blood cells and prevent anemia.[8]
Folate and folic acid derive their names from the Latin word folium, which means "leaf". Folate occurs naturally in many foods, and among plants are especially plentiful in dark green leafy vegetables.[9]
A lack of dietary folates can lead to folate deficiency. A complete lack of dietary folate takes months before deficiency develops as normal individuals have about 500–20,000 µg[10] of folate in body stores.[11] This deficiency can result in many health problems, the most notable one being neural tube defects in developing embryos. Common symptoms of folate deficiency include diarrhea, macrocytic anemia with weakness or shortness of breath, nerve damage with weakness and limb numbness (peripheral neuropathy),[12] pregnancy complications, mental confusion, forgetfulness or other cognitive declines, mental depression, sore or swollen tongue, peptic or mouth ulcers, headaches, heart palpitations, irritability, and behavioral disorders. Low levels of folate can also lead to homocysteine accumulation.[7] DNA synthesis and repair are impaired and this could lead to cancer development.[7]
Health benefits and risks
Pregnancy
Adequate folate intake during the preconception period (which is the time right before and just after a woman becomes pregnant) helps protect against a number of congenital malformations, including neural tube defects (which are the most notable birth defects that occur from folate deficiency).[13] Neural tube defects are severe abnormalities of the central nervous system that develop in babies during the first few weeks of pregnancy resulting in malformations of the spine, skull, and brain; the most common neural tube defects are spina bifida and anencephaly. The risk of neural tube defects is significantly reduced when supplemental folic acid is consumed in addition to a healthy diet before conception and during the first month after conception.[14][15] Supplementation with folic acid has also been shown to reduce the risk of congenital heart defects, cleft lips,[16] limb defects, and urinary tract anomalies.[17] Folate deficiency during pregnancy may also increase the risk of preterm delivery, infant low birth weight and fetal growth retardation, as well as increasing homocysteine level in the blood, which may lead to spontaneous abortion and pregnancy complications, such as placental abruption and pre-eclampsia.[18] Women who could become pregnant are advised to eat foods fortified with folic acid or take supplements in addition to eating folate-rich foods to reduce the risk of serious birth defects.[19] Taking 400 micrograms of synthetic folic acid daily from fortified foods and/or supplements has been suggested for all non-pregnant women, in order to have adequate folic acid intake even in case of unplanned pregnancies.[20] The RDA for folate equivalents for pregnant women is set at 600 micrograms,[21] although a range of 400 micrograms up to 4 milligrams (4000 micrograms) reported in an old U.S. Public Health Service guideline is still followed by many health care providers.[20][22][23][24] The mechanisms and reasons why folic acid prevents birth defects is unknown.[25] It is hypothesized that the insulin-like growth factor 2 gene is differentially methylated and these changes in IGF2 result in improved intrauterine growth and development.[25] Approximately 85% of women in an urban Irish study reported using folic acid supplements before they become pregnant, but only 18% used enough folic acid supplements to meet the current folic acid requirements due, it is reported, to socio-economic challenges.[26] Folic acid supplements may also protect the fetus against disease when the mother is battling a disease or taking medications or smoking during pregnancy.[27]
It also contributes to oocyte maturation, implantation, placentation, in addition to the general effects of folic acid and pregnancy. Therefore, it is necessary to receive sufficient amounts through the diet to avoid subfertility.[28]
There is growing concern worldwide that prenatal high folic acid in the presence of low vitamin B12 causes epigenetic changes in the unborn predisposing them to metabolic syndromes, central adiposity and adult diseases such as Type 2 diabetes.[29] Another active area of research and concern is that either too much or too little folic acid in utero causes epigenetic changes to the brain leading to autism spectrum disorders.[30][31][32]
Sperm quality
Folate is necessary for fertility in both men and women. It contributes to spermatogenesis. Therefore, it is necessary to receive sufficient amounts through the diet to avoid subfertility.[28] Also, polymorphisms in genes of enzymes involved in folate metabolism could be one reason for fertility complications in some women with unexplained infertility.[33]
Heart disease
Taking folic acid does not reduce cardiovascular disease even though it reduces homocysteine levels.[34]
Folic acid supplements consumed before and during pregnancy may reduce the risk of heart defects in infants.[35]
Stroke
Folic acid appears to reduce the risk of stroke, which may be due to the role folate plays in regulating homocysteine concentration. The reviews indicate the risk of stroke appears to be reduced only in some individuals, but a definite recommendation regarding supplementation beyond the current RDA has not been established for stroke prevention.[36] Observed stroke reduction is consistent with the reduction in pulse pressure produced by folate supplementation of 5 mg per day, since hypertension is a key risk factor for stroke. Folic supplements are inexpensive and relatively safe to use, which is why stroke or hyperhomocysteinemia patients are encouraged to consume daily B vitamins including folic acid.[37]
Cancer
Folic acid supplementation does not appear to affect the rate of cancer.[38][39]
Diets high in folate are associated with decreased risk of colorectal cancer; some studies show the association is stronger for folate from foods alone than for folate from foods and supplements,[40] One broad cancer screening trial reported a potential harmful effect of too much folate intake on breast cancer risk, suggesting routine folate supplementation should not be recommended as a breast cancer preventive.[41] Most research studies associate high dietary folate intake with a reduced risk of prostate cancer.[42]
Antifolates
Folate is important for cells and tissues that rapidly divide.[43] Cancer cells divide rapidly, and drugs that interfere with folate metabolism are used to treat cancer. The antifolate methotrexate is a drug often used to treat cancer because it inhibits the production of the active form of THF from the inactive dihydrofolate (DHF). However, methotrexate can be toxic,[44][45][46] producing side effects, such as inflammation in the digestive tract that make it difficult to eat normally. Also, bone marrow depression (inducing leukopenia and thrombocytopenia), and acute renal and hepatic failure have been reported.
Folinic acid, under the drug name leucovorin, a form of folate (formyl-THF), can help "rescue" or reverse the toxic effects of methotrexate.[47] Folinic acid is not the same as folic acid. Folic acid supplements have little established role in cancer chemotherapy.[48][49] There have been cases of severe adverse effects of accidental substitution of folic acid for folinic acid in patients receiving methotrexate cancer chemotherapy. It is important for anyone receiving methotrexate to follow medical advice on the use of folic or folinic acid supplements. The supplement of folinic acid in patients undergoing methotrexate treatment is to give cells dividing less rapidly enough folate to maintain normal cell functions. The amount of folate given will be depleted by rapidly dividing cells (cancer) very fast and so will not negate the effects of methotrexate.
Psychological
Some evidence links a shortage of folate with depression.[50] Limited evidence from randomised controlled trials showed using folic acid in addition to antidepressants, to be specific SSRIs, may have benefits.[51] Research at the University of York and Hull York Medical School has found a link between depression and low levels of folate.[52] One study by the same team involved 15,315 subjects.[53] However, the evidence is probably too limited at present for this to be a routine treatment recommendation. Folic acid supplementation affects noradrenaline and serotonin receptors within the brain, which could be the cause of folic acid's possible ability to act as an antidepressant.[54][55] The exact mechanisms involved in the development of schizophrenia are not entirely clear, but may have something to do with DNA methylation and one carbon metabolism, and these are the precise roles of folate in the body.[56]
Macular degeneration
A substudy of the Women's Antioxidant and Folic Acid Cardiovascular Study published in 2009 reported use of a nutritional supplement containing folic acid, pyridoxine, and cyanocobalamin decreased the risk of developing age-related macular degeneration by 34.7%.[57]
Folic Acid, B12 and Iron
There is a complex interaction between folic acid, vitamin B12 and iron. A deficiency of one may be "masked" by excess of another so the three must be in balance.[58][59][60]
Toxicity
The risk of toxicity from folic acid is low, because folate is a water-soluble vitamin and is regularly removed from the body through urine.[61] One potential issue associated with high dosages of folic acid is that it has a masking effect on the diagnosis of pernicious anaemia (vitamin B12 deficiency),[24] and a variety of concerns of potential negative impacts on health.[62]
Folate deficiency
Folate deficiency may lead to glossitis, diarrhea, depression, confusion, anemia, and fetal neural tube defects and brain defects (during pregnancy).[63] Folate deficiency is accelerated by alcohol consumption.[64] Folate deficiency is diagnosed by analyzing CBC and plasma vitamin B12 and folate levels.[63] CBC may indicate megaloblastic anemia but this could also be a sign of vitamin B12 deficiency.[63] A serum folate of 3 μg/L or lower indicates deficiency.[63] Serum folate level reflects folate status but erythrocyte folate level better reflects tissue stores after intake.[63] An erythrocyte folate level of 140 μg/L or lower indicates inadequate folate status.[63] Increased homocysteine level suggests tissue folate deficiency but homocysteine is also affected by vitamin B12 and vitamin B6, renal function, and genetics.[63] One way to differentiate between folate deficiency from vitamin B12 deficiency is by testing for methylmalonic acid levels.[63] Normal MMA levels indicate folate deficiency and elevated MMA levels indicate vitamin B12 deficiency.[63] Folate deficiency is treated with supplemental oral folate of 400 to 1000 μg per day.[63] This treatment is very successful in replenishing tissues, even if deficiency was caused by malabsorption.[63] Patients with megaloblastic anemia need to be tested for vitamin B12 deficiency before folate treatment, because if the patient has vitamin B12 deficiency, folate supplementation can remove the anemia, but can also worsen neurologic problems.[63] Morbidly obese patients with BMIs of greater than 50 are more likely to develop folate deficiency.[65] Patients with celiac disease have a higher chance of developing folate deficiency.[65] Cobalamin deficiency may lead to folate deficiency, which, in turn, increases homocysteine levels and may result in the development of cardiovascular disease or birth defects.[66]
Malaria
Some studies show iron-folic acid supplementation in children under 5 may result in increased mortality due to malaria; this has prompted the World Health Organization to alter their iron-folic acid supplementation policies for children in malaria-prone areas, such as India.[67]
Dietary reference intake
Because of the difference in bioavailability between supplemented folic acid and the different forms of folate found in food, the dietary folate equivalent (DFE) system was established. One DFE is defined as 1 μg (microgram) of dietary folate, or 0.6 μg of folic acid supplement.
| Age | Infants (RDI) | Infants (UL) | Adults (RDI) | Adults (UL) | Pregnant women (RDI) | Pregnant women (UL) | Lactating women (RDI) | Lactating women (UL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–6 months | 65 | None set | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 7–12 months | 80 | None set | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 1–3 years | – | – | 150 | 300 | – | – | – | – |
| 4–8 years | – | – | 200 | 400 | – | – | – | – |
| 9–13 years | – | – | 300 | 600 | – | – | – | – |
| 14–18 | – | – | 400 | 800 | 600 | 800 | 500 | 800 |
| 19+ | – | – | 400 | 1000 | 600 | 1000 | 500 | 1000 |
The Dietary Reference Intake (DRIs) were developed by the United States National Academy of Sciences to set reference values for planning and assessing nutrient intake for healthy people. DRIs incorporate two reference values, the Reference Daily Intake (RDI, the daily intake level that is adequate for 97–98% of the population in the United States where the standards were set) and tolerable upper intake levels (UL, the highest level of intake that is known to avoid toxicity). The UL for folate refers to only synthetic folate, as no health risks have been associated with high intake of folate from food sources.[68]
Sources
Folate naturally occurs in a wide variety of foods, including vegetables (particularly dark green leafy vegetables), fruits and fruit juices, nuts, beans, peas, dairy products, poultry and meat, eggs, seafood, grains, and some beers.[9][69] Spinach, liver, yeast, asparagus, and Brussels sprouts are among the foods with the highest levels of folate.[9]
Folic acid is added to grain products in many countries, and in these countries, fortified products make up a significant source of the population's folic acid intake.[70] Because of the difference in bioavailability between supplemented folic acid and the different forms of folate found in food, the dietary folate equivalent (DFE) system was established. 1 DFE is defined as 1 μg of dietary folate, or 0.6 μg of folic acid supplement. This is reduced to 0.5 μg of folic acid if the supplement is taken on an empty stomach.[71]
Folate naturally found in food is susceptible to high heat and ultraviolet light, and is soluble in water.[72] It is heat-labile in acidic environments and may also be subject to oxidation.[72]
Some meal replacement products do not meet the folate requirements as specified by the RDAs.[73]
Folate (B9) can also be processed from the pro-vitamin Pteroylmonoglutamic acid (Vitamin B10).
History
In the 1920s, scientists believed folate deficiency and anemia were the same condition.[74] A key observation by researcher Lucy Wills in 1931 led to the identification of folate as the nutrient needed to prevent anemia during pregnancy. Dr. Wills demonstrated anemia could be reversed with brewer's yeast. Folate was identified as the corrective substance in brewer's yeast in the late 1930s, and was first isolated in and extracted from spinach leaves by Mitchell and others in 1941.[75] Bob Stokstad isolated the pure crystalline form in 1943, and was able to determine its chemical structure while working at the Lederle Laboratories of the American Cyanamid Company.[76] This historical research project, of obtaining folic acid in a pure crystalline form in 1945, was done by the team called the "folic acid boys," under the supervision and guidance of Director of Research Dr. Yellapragada Subbarao, at the Lederle Lab, Pearl River, NY.[77] This research subsequently led to the synthesis of the antifolate aminopterin, the first-ever anticancer drug, the clinical efficacy was proven by Sidney Farber in 1948. In the 1950s and 1960s, scientists began to discover the biochemical mechanisms of action for folate.[74] In 1960, experts first linked folate deficiency to neural tube defects.[74] In the late 1990s, US scientists realized, despite the availability of folate in foods and in supplements, there was still a challenge for people to meet their daily folate requirements, which is when the US implemented the folate fortification program.[74]
Biological roles

DNA and cell division
Folate is necessary for the production and maintenance of new cells, for DNA synthesis and RNA synthesis, and for preventing changes to DNA, and, thus, for preventing cancer.[43] It is especially important during periods of frequent cell division and growth, such as infancy and pregnancy. Folate is needed to carry one-carbon groups for methylation reactions and nucleic acid synthesis (the most notable one being thymine, but also purine bases).[78] Thus, folate deficiency hinders DNA synthesis and cell division, affecting hematopoietic cells and neoplasms the most because of their greater frequency of cell division. RNA transcription, and subsequent protein synthesis, are less affected by folate deficiency, as the mRNA can be recycled and used again (as opposed to DNA synthesis, where a new genomic copy must be created). Since folate deficiency limits cell division, erythropoiesis, production of red blood cells, is hindered and leads to megaloblastic anemia, which is characterized by large immature red blood cells. This pathology results from persistently thwarted attempts at normal DNA replication, DNA repair, and cell division, and produces abnormally large red cells called megaloblasts (and hypersegmented neutrophils) with abundant cytoplasm capable of RNA and protein synthesis, but with clumping and fragmentation of nuclear chromatin. Some of these large cells, although immature (reticulocytes), are released early from the marrow in an attempt to compensate for the anemia.[79] Both adults and children need folate to make normal red and white blood cells and prevent anemia.[80] Deficiency of folate in pregnant women has been implicated in neural tube defects (NTD); therefore, many developed countries have implemented mandatory folic acid fortification in cereals, etc. NTDs occur early in pregnancy (first month), therefore women must have abundant folate upon conception. Folate is required to make red blood cells and white blood cells and folate deficiency may lead to anemia, which further leads to fatigue and weakness and inability to concentrate.[81]
Biochemistry of DNA base and amino acid production
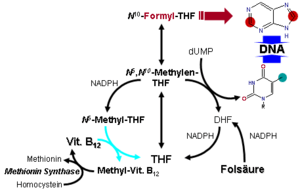
In the form of a series of tetrahydrofolate (THF) compounds, folate derivatives are substrates in a number of single-carbon-transfer reactions, and also are involved in the synthesis of dTMP (2′-deoxythymidine-5′-phosphate) from dUMP (2′-deoxyuridine-5′-phosphate). It is a substrate for an important reaction that involves vitamin B12 and it is necessary for the synthesis of DNA, and so required for all dividing cells.[17]
The pathway leading to the formation of tetrahydrofolate (FH4) begins when folic acid (F) is reduced to dihydrofolate (DHF) (FH2), which is then reduced to THF. Dihydrofolate reductase catalyses the last step.[82] Vitamin B3 in the form of NADPH is a necessary cofactor for both steps of the synthesis. Thus, hydride molecules are transferred from NADPH to the C6 position of the pteridine ring to reduce folic acid to THF.[83]
Methylene-THF (CH2FH4) is formed from THF by the addition of a methylene bridge from one of three carbon donors: formate, serine, or glycine. Methyl tetrahydrofolate (CH3-THF, or methyl-THF) can be made from methylene-THF by reduction of the methylene group with NADPH.
Another form of THF, 10-formyl-THF, results from oxidation of methylene-THF or is formed from formate donating formyl group to THF. Also, histidine can donate a single carbon to THF to form methenyl-THF.
Vitamin B12 is the only acceptor of methyl-THF, and this reaction produces methyl-B12 (methylcobalamin). There is also only one acceptor for methyl-B12, homocysteine, in a reaction catalyzed by homocysteine methyltransferase. These reactions are of importance because a defect in homocysteine methyltransferase or a deficiency of B12 may lead to a so-called "methyl-trap" of THF, in which THF is converted to a reservoir of methyl-THF which thereafter has no way of being metabolized, and serves as a sink of THF that causes a subsequent deficiency in folate.[76] Thus, a deficiency in B12 can generate a large pool of methyl-THF that is unable to undergo reactions and will mimic folate deficiency.
The reactions that lead to the methyl-THF reservoir can be shown in chain form:
- folate → dihydrofolate → tetrahydrofolate ↔ methylene-THF → methyl-THF

Conversion to biologically active derivatives
All the biological functions of folic acid are performed by tetrahydrofolate and other derivatives. Their biological availability to the body depends upon dihydrofolate reductase action in the liver. This action is unusually slow in humans, being less than 2% of that in rats. Moreover, in contrast to rats, an almost-5-fold variation in the activity of this enzyme exists between humans.[6] Due to this low activity, it has been suggested this limits the conversion of folic acid into its biologically active forms "when folic acid is consumed at levels higher than the Tolerable Upper Intake Level (1 mg/d for adults)."[6]
Overview of drugs that interfere with folate reactions
A number of drugs interfere with the biosynthesis of folic acid and THF. Among them are the dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors such as trimethoprim, pyrimethamine, and methotrexate; the sulfonamides (competitive inhibitors of 4-aminobenzoic acid in the reactions of dihydropteroate synthetase).
Valproic acid, one of the most commonly prescribed anticonvulsants that is also used to treat certain psychological conditions, is a known inhibitor of folic acid, and as such, has been shown to cause neural tube defects and cases of spina bifida and cognitive impairment in the newborn. Because of this considerable risk, those mothers who must continue to use valproic acid or its derivatives during pregnancy to control their condition (as opposed to stopping the drug or switching to another drug or to a lesser dose) should take folic acid supplements under the direction and guidance of their health care providers.
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III 1988–91) and the Continuing Survey of Food Intakes by Individuals (1994–96 CSFII) indicated most adults did not consume adequate folate.[84][85] However, the folic acid fortification program in the United States has increased folic acid content of commonly eaten foods such as cereals and grains, and as a result, diets of most adults now provide recommended amounts of folate equivalents.[86]
Dietary fortification

Folic acid fortification is a process where folic acid is added to flour with the intention of promoting public health through increasing blood folate levels in the populace. In the USA, food is fortified with folic acid, only one of the many naturally-occurring forms of folate, and a substance contributing only a minor amount to the folates in natural foods.[62]
Since the discovery of the link between insufficient folic acid and neural tube defects, governments and health organizations worldwide have made recommendations concerning folic acid supplementation for women intending to become pregnant.
Fortification is controversial, with issues having been raised concerning individual liberty,[62] as well as the health concerns described in the Toxicity section above. In the USA, there is concern that the federal government mandates fortification, but does not provide monitoring of potential undesirable effects of fortification.[62]
76 countries worldwide require mandatory folic acid fortification of at least one major cereal grain, with nearly all fortifying at least wheat flour, according to November 2013 data from the Flour Fortification Initiative.[87] These countries are:
- Antigua and Barbuda, Argentina, Australia, Bahamas, Bahrain, Barbados, Belize, Benin, Bolivia (Plurinational State of), Brazil, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cote d'Ivoire, Cuba, Dominica, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Egypt, El Salvador, Fiji, Ghana, Grenada, Guatemala, Guinea, Guyana, Haiti, Honduras, Indonesia, Iran (Islamic Republic of), Iraq, Jamaica, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kenya, Kosovo, Kuwait, Kyrgyzstan, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Mexico, Morocco, Nepal, Nicaragua, Niger, Nigeria, Oman, Palestine (Occupied Territory), Panama, Papua New Guinea, Paraguay, Peru, Republic of Moldova, Rwanda, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Saudi Arabia, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Solomon Islands, South Africa, Suriname, Tanzania (United Republic of), Togo, Trinidad and Tobago, Turkmenistan, Uganda, United States of America, Uruguay, Uzbekistan, and Yemen.[87]
As of November 2013, no EU country has mandated folic acid fortification.[87]
Australia
There has been previous debate in Australia regarding the inclusion of folic acid in products such as bread and flour.[88]
Australia and New Zealand have jointly agreed to fortification though the Food Standards Australia New Zealand. Australia will fortify all flour from 18 September 2009.[89] Although the food standard covers both Australia and New Zealand, an Australian government official has stated it is up to New Zealand to decide whether to implement it there, and they will watch with interest.[90]
The requirement is 0.135 mg of folate per 100g of bread.
Canada
In 2003, a Hospital for Sick Children, University of Toronto research group published findings showing the fortification of flour with folic acid in Canada has resulted in a dramatic decrease in neuroblastoma, an early and very dangerous cancer in young children.[91] In 2009, further evidence from McGill University showed a 6.2% decrease per year in the birth prevalence of severe congenital heart defects.[92]
Folic acid used in fortified foods is a synthetic form called pteroylmonoglutamate.[93] It is in its oxidized state and contains only one conjugated glutamate residue.[93] Folic acid therefore enters via a different carrier system from naturally occurring folate, and this may have different effects on folate binding proteins and its transporters.[94] Folic acid has a higher bioavailability than natural folates and are rapidly absorbed across the intestine,[93] therefore it is important to consider the Dietary Folate Equivalent (DFE) when calculating one's intake. Natural occurring folate is equal to 1 DFE, however 0.6 µg of folic acid is equal to 1 DFE.
Folic acid food fortification became mandatory in Canada in 1998, with the fortification of 150 µg of folic acid per 100 grams of enriched flour and uncooked cereal grains.[95] The purpose of fortification was to decrease the risk of neural tube defects in newborns.[95] It is important to fortify grains because it is a widely eaten food and the neural tube closes in the first four weeks of gestation, often before many women even know they are pregnant. Canada's fortification program has been successful with a decrease of neural tube defects by 19% since its introduction.[96] A seven-province study from 1993 to 2002 showed a reduction of 46% in the overall rate of neural tube defects after folic acid fortification was introduced in Canada.[97] The fortification program was estimated to raise a person’s folic acid intake level by 70–130 µg/day, however an increase of almost double that amount was actually observed.[96] This could be from the fact that many foods are over fortified by 160–175% the predicted value.[96] In addition, much of the elder population take supplements that adds 400 µg to their daily folic acid intake. This is a concern because 70–80% of the population have detectable levels of unmetabolized folic acid in their blood and high intakes can accelerate the growth of preneoplasmic lesions.[98] It is still unknown the amount of folic acid supplementation that might cause harm.[95]
Supplementation promotion
According to a Canadian survey, 58% of women said they took a folic acid containing multivitamin or a folic acid supplement as early as three months before becoming pregnant. Women in higher income households and with more years of school education are using more folic acid supplements before pregnancy. Women with planned pregnancies and who are over the age of 25 are more likely to use folic acid supplement. Canadian public health efforts are focused on promoting awareness of the importance of folic acid supplementation for all women of childbearing age and decreasing socio-economic inequalities by providing practical folic acid support to vulnerable groups of women.[97]
New Zealand
New Zealand was planning to fortify bread (excluding organic and unleavened varieties) from 18 September 2009, but has opted to wait until more research is done.[89]
The Association of Bakers [99] and the Green Party [100] have opposed mandatory fortification, describing it as "mass medication". Food Safety Minister Kate Wilkinson reviewed the decision to fortify in July 2009, citing links between overconsumption of folate with cancer .[101] The New Zealand Government is reviewing whether it will continue with the mandatory introduction of folic acid to bread.[102]
United Kingdom
There has been previous debate in the United Kingdom regarding the inclusion of folic acid in products such as bread and flour.[103] While the Food Standards Agency has recommended folic acid fortification,[104][105][106] and wheat flour is fortified with iron,[87] folic acid fortification of wheat flour is allowed voluntarily rather than required.
United States
The United States Public Health Service recommends an extra 0.4 mg/day for newly pregnant women, which can be taken as a pill. However, many researchers believe supplementation in this way can never work effectively enough, since about half of all pregnancies in the U.S. are unplanned, and not all women will comply with the recommendation. Approximately 53% of the US population uses dietary supplements and 35% uses dietary supplements containing folic acid.[107] Men consume more folate (in dietary folate equivalents) than women, and non-Hispanic whites have higher folate intakes than Mexican Americans and non-Hispanic blacks.[107] Twenty nine percent of black women have inadequate intakes of folate.[107] The age group consuming the most folate and folic acid is the >50 group.[107] 5% of the population exceeds the Tolerable Upper Intake Level.[107]
In 1996, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) published regulations requiring the addition of folic acid to enriched breads, cereals, flours, corn meals, pastas, rice, and other grain products.[108][109] This ruling took effect on January 1, 1998, and was specifically targeted to reduce the risk of neural tube birth defects in newborns.[110] There are concerns that the amount of folate added is insufficient .[111] In October 2006, the Australian press claimed that U.S. regulations requiring fortification of grain products were being interpreted as disallowing fortification in non-grain products, specifically Vegemite (an Australian yeast extract containing folate). The FDA later said the report was inaccurate, and no ban or other action was being taken against Vegemite.[112]
As a result of the folic acid fortification program, fortified foods have become a major source of folic acid in the American diet.[9] The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, Georgia used data from 23 birth defect registries covering about half of United States births, and extrapolated their findings to the rest of the country. These data indicate since the addition of folic acid in grain-based foods as mandated by the FDA, the rate of neural tube defects dropped by 25% in the United States.[113] The results of folic acid fortification on the rate of neural tube defects in Canada have also been positive, showing a 46% reduction in prevalence of NTDs;[114] the magnitude of reduction was proportional to the prefortification rate of NTDs, essentially removing geographical variations in rates of NTDs seen in Canada before fortification.
When the U.S. Food and Drug Administration set the folic acid fortification regulation in 1996, the projected increase in folic acid intake was 100 µg/d.[115] Data from a study with 1480 subjects showed that folic acid intake increased by 190 µg/d and total folate intake increased by 323 µg dietary folate equivalents (DFE)/d.[115] Folic acid intake above the upper tolerable intake level (1000 µg folic acid/d) increased only among those individuals consuming folic acid supplements as well as folic acid found in fortified grain products.[115] Taken together, folic acid fortification has led to a bigger increase in folic acid intake than first projected.[115]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Folic acid in the ChemIDplus database
- ↑ R. M. C. Dawson: Data for Biochemical Research, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1989, 3rd Edition, p. 134, ISBN 0-19-855299-8.
- ↑ Ural, Serdar H. (2008-11). "Folic Acid and Pregnancy". Kid's Health.
- ↑ "Definition of vitamin Bc". Medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com. Retrieved 2012-09-09.
- ↑ "Folate". Patient Care & Health Info – Drugs and Supplements. Mayo Clinic. 1 November 2013. Retrieved 11 January 2014.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Bailey SW, Ayling JE (September 2009). "The extremely slow and variable activity of dihydrofolate reductase in human liver and its implications for high folic acid intake". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106 (36): 15424–9. Bibcode:2009PNAS..10615424B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0902072106. PMC 2730961. PMID 19706381.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Weinstein SJ, Hartman TJ, Stolzenberg-Solomon R, et al. (November 2003). "Null association between prostate cancer and serum folate, vitamin B(6), vitamin B(12), and homocysteine". Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 12 (11 Pt 1): 1271–2. PMID 14652294.
- ↑ "Dietary Supplement Fact Sheet: Folate". Office of Dietary Supplements, National Institutes of Health.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 "Dietary supplement fact sheet: Folate". Health Information. Office of Dietary Supplements, US National Institutes of Health. Retrieved 11 January 2014.
- ↑ Gentili et al, 2009, Folic Acid Deficiency http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/200184-overview
- ↑ National Health Service U.K., "Anaemia, vitamin B12 or folate deficiency – Causes" http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Anaemia-vitamin-B12-and-folate-deficiency/Pages/Causes.aspx
- ↑ Botez MI (1976). "Folate deficiency and neurological disorders in adults". Med. Hypotheses 2 (4): 135–40. doi:10.1016/0306-9877(76)90068-2. PMID 958035.
- ↑ Shaw GM, Schaffer D, Velie EM, Morland K, Harris JA (May 1995). "Periconceptional vitamin use, dietary folate, and the occurrence of neural tube defects". Epidemiology 6 (3): 219–26. doi:10.1097/00001648-199505000-00005. PMID 7619926.
- ↑ Mulinare J, Cordero JF, Erickson JD, Berry RJ (December 1988). "Periconceptional use of multivitamins and the occurrence of neural tube defects". JAMA 260 (21): 3141–5. doi:10.1001/jama.1988.03410210053035. PMID 3184392.
- ↑ Milunsky A, Jick H, Jick SS, Bruell CL, MacLaughlin DS, Rothman KJ, Willett W (1989). "Multivitamin/folic acid supplementation in early pregnancy reduces the prevalence of neural tube defects". Journal of the American Medical Association 262 (20): 2847–2852. doi:10.1001/jama.262.20.2847. PMID 2478730.
- ↑ Wilcox AJ, Lie RT, Solvoll K, et al. (March 2007). "Folic acid supplements and risk of facial clefts: national population based case-control study". BMJ 334 (7591): 464. doi:10.1136/bmj.39079.618287.0B. PMC 1808175. PMID 17259187.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Goh YI, Koren G (January 2008). "Folic acid in pregnancy and fetal outcomes". J Obstet Gynaecol 28 (1): 3–13. doi:10.1080/01443610701814195. PMID 18259891.
- ↑ Scholl TO, Johnson WG (May 2000). "Folic acid: influence on the outcome of pregnancy". Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 71 (5 Suppl): 1295S–303S. PMID 10799405.
- ↑ Wilton DC, Foureur MJ (June 2010). "A survey of folic acid use in primigravid women". Women Birth 23 (2): 67–73. doi:10.1016/j.wombi.2009.09.001. PMID 19828392.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Health Professionals Recommendations, Folic Acid, NCBDDD, CDC
- ↑ United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). 2010. Dietary Guidelines for Americans. 7th ed. Government Printing Office , Washington, DC, U.S.
- ↑ "Recommendations for the use of folic acid to reduce the number of cases of spina bifida and other neural tube defects". MMWR Recomm Rep 41 (RR–14): 1–7. September 1992. PMID 1522835.
- ↑ Centers for Disease Control (CDC) (August 1991). "Use of folic acid for prevention of spina bifida and other neural tube defects--1983-1991". MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 40 (30): 513–6. PMID 2072886.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 FAO; WHO (2002). "4 Folate and Folic Acid". Human Vitamin and Mineral Requirements.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 Steegers-Theunissen RP, Obermann-Borst SA, Kremer D, et al. (2009). "Periconceptional maternal folic acid use of 400 microg per day is related to increased methylation of the IGF2 gene in the very young child". In Zhang, Cuilin. PLoS ONE 4 (11): e7845. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0007845. PMC 2773848. PMID 19924280.
- ↑ McGuire M, Cleary B, Sahm L, Murphy DJ (February 2010). "Prevalence and predictors of periconceptional folic acid uptake--prospective cohort study in an Irish urban obstetric population". Hum. Reprod. 25 (2): 535–43. doi:10.1093/humrep/dep398. PMID 19910320.
- ↑ Jia ZL, Li Y, Chen CH, et al. (January 2010). "Association among polymorphisms at MYH9, environmental factors, and nonsyndromic orofacial clefts in western China". DNA Cell Biol. 29 (1): 25–32. doi:10.1089/dna.2009.0935. PMID 19891592.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 Ebisch IM, Thomas CM, Peters WH, Braat DD, Steegers-Theunissen RP (2007). "The importance of folate, zinc and antioxidants in the pathogenesis and prevention of subfertility". Hum. Reprod. Update 13 (2): 163–74. doi:10.1093/humupd/dml054. PMID 17099205.
- ↑ Yajnik CS, Deshmukh US (September 2008). "Maternal nutrition, intrauterine programming and consequential risks in the offspring". Rev Endocr Metab Disord 9 (3): 203–11. doi:10.1007/s11154-008-9087-z. PMID 18661241.
- ↑ Beard CM, Panser LA, Katusic SK (July 2011). "Is excess folic acid supplementation a risk factor for autism?". Med. Hypotheses 77 (1): 15–7. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2011.03.013. PMID 21454018.
- ↑ Jon Hamilton. "Folic Acid For Pregnant Mothers Cuts Kids' Autism Risk". NPR. Retrieved 2013-03-08.
- ↑ "Does Folic Acid Help Prevent Autism?". Kidsdr.com. Retrieved 2013-07-25.
- ↑ Altmäe S, Stavreus-Evers A, Ruiz JR, et al. (June 2010). "Variations in folate pathway genes are associated with unexplained female infertility". Fertil. Steril. 94 (1): 130–7. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.02.025. PMID 19324355.
- ↑ Bazzano LA (August 2011). "No effect of folic acid supplementation on cardiovascular events, cancer or mortality after 5 years in people at increased cardiovascular risk, although homocysteine levels are reduced". Evid Based Med 16 (4): 117–8. doi:10.1136/ebm1204. PMID 21402567.
- ↑ Bazzano LA (July 2009). "Folic acid supplementation and cardiovascular disease: the state of the art". Am. J. Med. Sci. 338 (1): 48–9. doi:10.1097/MAJ.0b013e3181aaefd6. PMID 19593104.
- ↑ "Folic acid 'reduces stroke risks'". BBC News (London). 31 May 2007.
- ↑ Terwecoren A, Steen E, Benoit D, Boon P, Hemelsoet D (September 2009). "Ischemic stroke and hyperhomocysteinemia: truth or myth?". Acta Neurol Belg 109 (3): 181–8. PMID 19902811.
- ↑ Vollset, SE; Clarke, R; Lewington, S; Ebbing, M; Halsey, J; Lonn, E; Armitage, J; Manson, JE; Hankey, GJ; Spence, JD; Galan, P; Bønaa, KH; Jamison, R; Gaziano, JM; Guarino, P; Baron, JA; Logan, RF; Giovannucci, EL; den Heijer, M; Ueland, PM; Bennett, D; Collins, R; Peto, R; for the B-Vitamin Treatment Trialists', Collaboration (Jan 24, 2013). "Effects of folic acid supplementation on overall and site-specific cancer incidence during the randomised trials: meta-analyses of data on 50 000 individuals". Lancet 381 (9871): 1029–36. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)62001-7. PMID 23352552.
- ↑ Clarke R, Halsey J, Lewington S, et al. (October 2010). "Effects of lowering homocysteine levels with B vitamins on cardiovascular disease, cancer, and cause-specific mortality: Meta-analysis of 8 randomized trials involving 37 485 individuals". Arch. Intern. Med. 170 (18): 1622–31. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2010.348. PMID 20937919.
- ↑ Sanjoaquin MA, Allen N, Couto E, Roddam AW, Key TJ (February 2005). "Folate intake and colorectal cancer risk: a meta-analytical approach". Int. J. Cancer 113 (5): 825–8. doi:10.1002/ijc.20648. PMID 15499620.
- ↑ Kim YI (October 2006). "Does a high folate intake increase the risk of breast cancer?". Nutr. Rev. 64 (10 Pt 1): 468–75. doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2006.tb00178.x. PMID 17063929.
- ↑ Johansson M, Appleby PN, Allen NE, et al. (February 2008). "Circulating concentrations of folate and vitamin B12 in relation to prostate cancer risk: results from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition study". Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 17 (2): 279–85. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-07-0657. PMID 18268110.
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 Kamen B (October 1997). "Folate and antifolate pharmacology". Semin. Oncol. 24 (5 Suppl 18): S18–30–S18–39. PMID 9420019.
- ↑ Rubio IT, Cao Y, Hutchins LF, Westbrook KC, Klimberg VS (May 1998). "Effect of glutamine on methotrexate efficacy and toxicity". Ann. Surg. 227 (5): 772–8; discussion 778–80. doi:10.1097/00000658-199805000-00018. PMC 1191365. PMID 9605669.
- ↑ Wolff JE, Hauch H, Kuhl J, Egeler RM, Jurgens H (1998). "Dexamethasone increases hepatotoxicity of MTX in children with brain tumors". Anticancer Research 18 (4B): 2895–9. PMID 9713483.
- ↑ Kepka L, De Lassence A, Ribrag V, et al. (March 1998). "Successful rescue in a patient with high dose methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity and acute renal failure". Leuk. Lymphoma 29 (1–2): 205–9. doi:10.3109/10428199809058397. PMID 9638991.
- ↑ Branda RF, Nigels E, Lafayette AR, Hacker M. (1998). "Nutritional folate status influences the efficacy and toxicity of chemotherapy in rats". Blood 92 (7): 2471–6. PMID 9746787.
- ↑ Shiroky JB; Frcp(c) (November 1997). "The use of folates concomitantly with low-dose pulse methotrexate". Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 23 (4): 969–80. doi:10.1016/S0889-857X(05)70369-0. PMID 9361164.
- ↑ Keshava C, Keshava N, Whong WZ, Nath J, Ong TM (February 1998). "Inhibition of methotrexate-induced chromosomal damage by folinic acid in V79 cells". Mutat. Res. 397 (2): 221–8. doi:10.1016/S0027-5107(97)00216-9. PMID 9541646.
- ↑ Coppen A, Bolander-Gouaille C (January 2005). "Treatment of depression: time to consider folic acid and vitamin B12". J. Psychopharmacol. (Oxford) 19 (1): 59–65. doi:10.1177/0269881105048899. PMID 15671130.
- ↑ Taylor MJ, Carney SM, Goodwin GM, Geddes JR (June 2004). "Folate for depressive disorders: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials". J. Psychopharmacol. (Oxford) 18 (2): 251–6. doi:10.1177/0269881104042630. PMID 15260915.
- ↑ Gilbody S, Lewis S, Lightfoot T (January 2007). "Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) genetic polymorphisms and psychiatric disorders: a HuGE review". Am. J. Epidemiol. 165 (1): 1–13. doi:10.1093/aje/kwj347. PMID 17074966.
- ↑ Gilbody S, Lightfoot T, Sheldon T (July 2007). "Is low folate a risk factor for depression? A meta-analysis and exploration of heterogeneity". J Epidemiol Community Health 61 (7): 631–7. doi:10.1136/jech.2006.050385. PMC 2465760. PMID 17568057.
- ↑ Gaweesh S, Ewies AA (February 2010). "Folic acid supplementation cures hot flushes in postmenopausal women". Med. Hypotheses 74 (2): 286–8. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2009.09.010. PMID 19796883.
- ↑ García-Miss Mdel R, Pérez-Mutul J, López-Canul B, et al. (May 2010). "Folate, homocysteine, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor alfa levels, but not the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T polymorphism, are risk factors for schizophrenia". J Psychiatr Res 44 (7): 441–6. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2009.10.011. PMID 19939410.
- ↑ Krebs MO, Bellon A, Mainguy G, Jay TM, Frieling H (December 2009). "One-carbon metabolism and schizophrenia: current challenges and future directions". Trends Mol Med 15 (12): 562–70. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2009.10.001. PMID 19896901.
- ↑ Christen WG, Glynn RJ, Chew EY, Albert CM, Manson JE (February 2009). "Folic acid, pyridoxine, and cyanocobalamin combination treatment and age-related macular degeneration in women: the Women's Antioxidant and Folic Acid Cardiovascular Study". Arch. Intern. Med. 169 (4): 335–41. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2008.574. PMC 2648137. PMID 19237716.
- ↑ Vreugdenhil G, Wognum AW, van Eijk HG, Swaak AJ (February 1990). "Anaemia in rheumatoid arthritis: the role of iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid deficiency, and erythropoietin responsiveness". Ann. Rheum. Dis. 49 (2): 93–8. doi:10.1136/ard.49.2.93. PMC 1003985. PMID 2317122.
- ↑ Reynolds E (November 2006). "Vitamin B12, folic acid, and the nervous system". Lancet Neurol 5 (11): 949–60. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(06)70598-1. PMID 17052662.
- ↑ Allen RH, Stabler SP, Savage DG, Lindenbaum J (June 1990). "Diagnosis of cobalamin deficiency I: usefulness of serum methylmalonic acid and total homocysteine concentrations". Am. J. Hematol. 34 (2): 90–8. doi:10.1002/ajh.2830340204. PMID 2339683.
- ↑ Hathcock JN (August 1997). "Vitamins and minerals: efficacy and safety". Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 66 (2): 427–37. PMID 9250127.
- ↑ 62.0 62.1 62.2 62.3 Smith AD (January 2007). "Folic acid fortification: the good, the bad, and the puzzle of vitamin B-12". Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 85 (1): 3–5. PMID 17209170.
- ↑ 63.0 63.1 63.2 63.3 63.4 63.5 63.6 63.7 63.8 63.9 63.10 63.11 http://www.merck.com
- ↑ Diaz, V. H. US Patent 20080020071, Jan 24, 2008.
- ↑ 65.0 65.1 Malterre T (September 2009). "Digestive and nutritional considerations in celiac disease: could supplementation help?". Altern Med Rev 14 (3): 247–57. PMID 19803549.
- ↑ Varela-Moreiras G, Murphy MM, Scott JM (May 2009). "Cobalamin, folic acid, and homocysteine". Nutr. Rev. 67 Suppl 1: S69–72. doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2009.00163.x. PMID 19453682.
- ↑ Pasricha S, Shet A, Sachdev HP, Shet AS (October 2009). "Risks of routine iron and folic acid supplementation for young children". Indian Pediatr 46 (10): 857–66. PMID 19887691.
- ↑ 68.0 68.1 "Dietary Supplement Fact Sheet: Folate". National Institutes of Health.
- ↑ Owens, Janel E.; Clifford, Andrew J.; Bamforth, Charles W. (2007). "Folate in Beer". Journal of the Institute of Brewing 113 (3): 243–248. doi:10.1002/j.2050-0416.2007.tb00283.x. ISSN 0046-9750.
- ↑ Dietrich, M; Brown, CJ; Block, G (2005). "The effect of folate fortification of cereal-grain products on blood folate status, dietary folate intake, and dietary folate sources among adult non-supplement users in the United States". J Am Coll Nutr 24 (4): 266–274. doi:10.1080/07315724.2005.10719474. PMID 16093404.
- ↑ Suitor, CW; Bailey, LB (2000). "Dietary folate equivalents: interpretation and application". J Am Diet Assoc 100 (1): 88–94. doi:10.1016/S0002-8223(00)00027-4. PMID 10646010.
- ↑ 72.0 72.1 "Effects of Cooking on Vitamins (Table)". Beyondveg.com. Retrieved 2012-09-09.
- ↑ Cabanillas, M; Moya Chimenti, E; González Candela, C; Loria Kohen, V; Dassen, C; Lajo, T. (2009). "Usefulness of meal replacement: analysis of the principal meal replacement products commercialised in Spain". Nutr Hosp. 24 (5): 535–42. PMID 19893863.
- ↑ 74.0 74.1 74.2 74.3 Lanska, DJ. (2009). "Chapter 30 Historical aspects of the major neurological vitamin deficiency disorders: the water-soluble B vitamins". Handb Clin Neurol. Handbook of Clinical Neurology 95: 445–76. doi:10.1016/S0072-9752(08)02130-1. ISBN 978-0-444-52009-8. PMID 19892133.
- ↑ Mitchell HK, Snell EE, Williams RJ (1941). "The concentration of "folic acid"". J Am Chem Soc. 63 (8): 2284. doi:10.1021/ja01853a512.
- ↑ 76.0 76.1 Hoffbrand AV, Weir DG (June 2001). "The history of folic acid". Br. J. Haematol. 113 (3): 579–89. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2141.2001.02822.x. PMID 11380441.
- ↑ Angier RB, Boothe JH, Hutchings BL, et al. (August 1945). "Synthesis of a Compound Identical with the L. Casei Factor Isolated from Liver". Science 102 (2644): 227–8. Bibcode:1945Sci...102..227A. doi:10.1126/science.102.2644.227. PMID 17778509.
- ↑ Figueiredo JC, Grau MV, Haile RW, et al. (March 2009). "Folic acid and risk of prostate cancer: results from a randomized clinical trial". J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 101 (6): 432–5. doi:10.1093/jnci/djp019. PMC 2657096. PMID 19276452.
- ↑ Smith C, Lieberman M, Marks DB, Marks AD (2007). Marks' essential medical biochemistry. Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0-7817-9340-8.
- ↑ Zittoun J (1993). "Anemias due to disorder of folate, vitamin B12 and transcobalamin metabolism". La Revue du praticien 43 (11): 1358–63. PMID 8235383. (French)
- ↑ "Folate and Your Health - HealthLinkBC File #68g". Healthlinkbc.ca. Retrieved 2012-09-09.
- ↑ "EC 1.5.1.3". Us.expasy.org. Retrieved 2012-09-09.
- ↑ Benkovic SJ, Hammes-Schiffer S (August 2003). "A perspective on enzyme catalysis". Science 301 (5637): 1196–202. Bibcode:2003Sci...301.1196B. doi:10.1126/science.1085515. PMID 12947189.
- ↑ Alaimo K, McDowell MA, Briefel RR, Bischof AM, Caughman CR, Loria CM, Johnson CL (1994). "Dietary intake of vitamins, minerals, and fiber of persons ages 2 months and over in the United States: Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, Phase 1, 1988–91". Advance Data from Vital and Health Statistics (258): 1–28. PMID 10138938.
- ↑ Raiten DJ, Fisher KD (1995). "Assessment of folate methodology used in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III, 1988–1994)". The Journal of Nutrition 125 (5): 1371S–1398S. PMID 7738698.
- ↑ Lewis CJ, Crane NT, Wilson DB, Yetley EA (August 1999). "Estimated folate intakes: data updated to reflect food fortification, increased bioavailability, and dietary supplement use". Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 70 (2): 198–207. PMID 10426695.
- ↑ 87.0 87.1 87.2 87.3 "Global Progress". Flour Fortification Initiative website. Flour Fortificatoin Initiative. November 2013.
- ↑ "Bread fortification 'not justified'". The Sydney Morning Herald. 29 July 2006.
- ↑ 89.0 89.1 NZPA (2007-06-22). "Bread to be fortified with folic acid". NZ Herald. Retrieved 2009-07-13.
- ↑ "Bread additive call 'up to NZ'". Retrieved 2009-07-15.
- ↑ French AE, Grant R, Weitzman S, et al. (September 2003). "Folic acid food fortification is associated with a decline in neuroblastoma". Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 74 (3): 288–94. doi:10.1016/S0009-9236(03)00200-5. PMID 12966372.
- ↑ Ionescu-Ittu R, Marelli AJ, Mackie AS, Pilote L (2009). "Prevalence of severe congenital heart disease after folic acid fortification of grain products: time trend analysis in Quebec, Canada". BMJ 338: b1673. doi:10.1136/bmj.b1673. PMC 2682153. PMID 19436079.
- ↑ 93.0 93.1 93.2 Smith AD, Kim YI, Refsum H (March 2008). "Is folic acid good for everyone?". Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 87 (3): 517–33. PMID 18326588.
- ↑ Ulrich CM, Potter JD (February 2006). "Folate supplementation: too much of a good thing?". Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 15 (2): 189–93. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-152CO. PMID 16492904.
- ↑ 95.0 95.1 95.2 Mason JB, Dickstein A, Jacques PF, et al. (July 2007). "A temporal association between folic acid fortification and an increase in colorectal cancer rates may be illuminating important biological principles: a hypothesis". Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 16 (7): 1325–9. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-07-0329. PMID 17626997.
- ↑ 96.0 96.1 96.2 Quinlivan EP, Gregory JF (January 2003). "Effect of food fortification on folic acid intake in the United States". Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 77 (1): 221–5. PMID 12499345.
- ↑ 97.0 97.1 "Welcome to the Health Canada Web site". Hc-sc.gc.ca. Retrieved 2012-09-09.
- ↑ Chustecka, Z. (2009 Retrieved 11/09, 2009). Folic-acid fortification of flour and increased rates of colon cancer.
- ↑ "Work Starts on Wilkinson’s Mass Medication Plan" (Press release). Association Of Bakers. 2009-07-08. Retrieved 2009-07-13.
- ↑ "NZ should push pause on folic fortification" (Press release). Green Party. 2009-07-09. Retrieved 2009-07-13.
- ↑ NZPA (2009-07-08). "Bakers, Govt battle over folic acid". NZ Herald. Retrieved 2009-07-13.
- ↑ "Govt reviewing folic acid policy". Stuff. Retrieved 15 July 2009.
- ↑ BBC 'Put folic acid in bread' 2000-01-13
- ↑ FSA (2007-05-17). "Board recommends mandatory fortification". Retrieved 2007-05-18.
- ↑ "Backing for folic acid in bread". BBC News. 17 May 2007. Retrieved 2007-05-18.
- ↑ BBC Experts back folic acid in flour 11 May 2007
- ↑ 107.0 107.1 107.2 107.3 107.4 Bailey RL, Dodd KW, Gahche JJ, et al. (January 2010). "Total folate and folic acid intake from foods and dietary supplements in the United States: 2003-2006". Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 91 (1): 231–7. doi:10.3945/ajcn.2009.28427. PMC 2793110. PMID 19923379.
- ↑ Malinow MR, Duell PB, Hess DL, et al. (April 1998). "Reduction of plasma homocyst(e)ine levels by breakfast cereal fortified with folic acid in patients with coronary heart disease". N. Engl. J. Med. 338 (15): 1009–15. doi:10.1056/NEJM199804093381501. PMID 9535664.
- ↑ Daly S, Mills JL, Molloy AM, et al. (December 1997). "Minimum effective dose of folic acid for food fortification to prevent neural-tube defects". Lancet 350 (9092): 1666–9. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(97)07247-4. PMID 9400511.
- ↑ Crandall BF, Corson VL, Evans MI, Goldberg JD, Knight G, Salafsky IS (July 1998). "American College of Medical Genetics statement on folic acid: fortification and supplementation". Am. J. Med. Genet. 78 (4): 381. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19980724)78:4<381::AID-AJMG16>3.0.CO;2-E. PMID 9714444.
- ↑ "FDA muffed chance to reduce birth defects". Boston Globe. 6 January 2004.
- ↑ "US denies Vegemite ban". 25 October 2006. Archived from the original on 2009-03-01.
- ↑ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (May 2004). "Spina bifida and anencephaly before and after folic acid mandate--United States, 1995-1996 and 1999-2000". MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 53 (17): 362–5. PMID 15129193.
- ↑ De Wals P, Tairou F, Van Allen MI, et al. (July 2007). "Reduction in neural-tube defects after folic acid fortification in Canada". N. Engl. J. Med. 357 (2): 135–42. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa067103. PMID 17625125.
- ↑ 115.0 115.1 115.2 115.3 Choumenkovitch SF, Selhub J, Wilson PW, Rader JI, Rosenberg IH, Jacques PF (September 2002). "Folic acid intake from fortification in United States exceeds predictions". J. Nutr. 132 (9): 2792–8. PMID 12221247.
Bibliography
- This article contains information from the public domain resource at http://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Folate-HealthProfessional/
- Herbert V (1999). "Folic Acid". In Shils ME, Olson J, Shike M, Ross AC. Modern nutrition in health and disease (9th ed.). Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins. ISBN 0-683-30769-X.
- Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine (1998). Dietary reference intakes for thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin B6, folate, vitamin B12, pantothenic acid, biotin, and choline / a report of the Standing Committee on the Scientific Evaluation of Dietary Reference Intakes and its Panel on Folate, Other B Vitamins, and Choline and Subcommittee on Upper Reference Levels of Nutrients. Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press. ISBN 0-309-06554-2.
- Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee, Agricultural Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Report of the Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee on the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2010. http://www.cnpp.usda.gov/dgas2010-dgacreport.htm
External links
- Jane Higdon, "Folic Acid", Micronutrient Information Center, Linus Pauling Institute, Oregon State University
- Health Canada article about folic acid
- Folic Acid Council of Canada
- US Public Health Service information page on folic acid
- The primary prevention of birth defects: Multivitamins or folic acid?
- Folate and Vitamin B12 at Lab Tests Online
- Biochemistry links
- Folate biosynthesis (early stages)
- Folate biosynthesis (later stages)
- Folate coenzymes
- C1 metabolism with folate
- Formylation, hydroxymethylation and methylation using folate
- IUPAC nomenclature of folate related compounds
| ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||