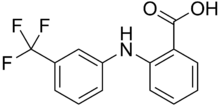
Flufenamic acid
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| 2-{[3-(Trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino}benzoic acid | |
| Clinical data | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Legal status | Prescription Only (S4) (AU) |
| Routes | oral, topical |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | extensively |
| Metabolism | Hydroxylation, glucuronidation |
| Half-life | ~3 h |
| Excretion | 50% urine, 36% feces |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 530-78-9 |
| ATC code | M01AG03 |
| PubChem | CID 3371 |
| IUPHAR ligand | 2447 |
| DrugBank | DB02266 |
| ChemSpider | 3254 |
| UNII | 60GCX7Y6BH |
| KEGG | D01581 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:42638 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL23588 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C14H10F3NO2 |
| Mol. mass | 281.22991 g/mol |
| SMILES
| |
| |
| Physical data | |
| Melt. point | 124–125 °C (255–257 °F) resolidification and remelting at 134°C to 136°C |
| Solubility in water | Practically insoluble in water; soluble in ethanol, chloroform and diethyl ether mg/mL (20 °C) |
| | |
Flufenamic acid, also known as Fluffy or Fluf[citation needed], is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug.[1] It is pale yellow crystalline powder.
Flufenamic acid also blocks voltage-gated sodium channels responsible for the depolarising after-potential (DAP) that underlies phasic firing in the phasic firing of magnocellular neurons in the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei.[citation needed]
References
- ↑ Lovering, A. L.; Ride, J. P.; Bunce, C. M.; Desmond, J. C.; Cummings, S. M.; White, S. A. (2004). "Crystal structures of prostaglandin D(2) 11-ketoreductase (AKR1C3) in complex with the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs flufenamic acid and indomethacin". Cancer research 64 (5): 1802–1810. PMID 14996743.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.