Flosequinan
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
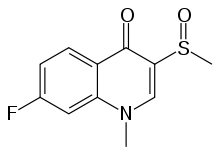 | |
|---|---|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| (RS)-7-fluoro-3-methanesulfinyl-1-methyl-1,4-dihydroquinolin-4-one | |
| Clinical data | |
| Legal status | ? |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 76568-02-0 |
| ATC code | C01DB01 |
| PubChem | CID 4474062 |
| UNII | 6NB119DLU7 |
| KEGG | D04195 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C11H10FNO2S |
| Mol. mass | 239.267 g/mol |
| | |
Flosequinan is a quinolone vasodilator. It has direct relaxing effects on peripheral arteries and veins. It is administered orally in cases of congestive heart failure in patients who are not responsive to digitalis or ACE inhibitors. It was sold under the trade name Manoplax.
It was withdrawn from the US market in October 1993 due to an increased risk of hospitalization or death.[1]
References
- ↑ "Heart drug withdrawn - Boots Pharmaceuticals' Manoplax". FDA Consumer. 1993. Retrieved 2008-12-01.
| ||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.