Flocoumafen
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Flocoumafen | ||
|---|---|---|
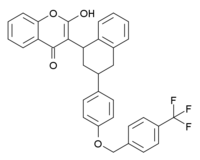 | ||
| IUPAC name 2-Hydroxy-3-[3-[4-([4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methoxy)phenyl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-yl] chromen-4-one | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 90035-08-8 | |
| PubChem | 91748 | |
| KEGG | C18696 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 | |
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C33H25F3O4 | |
| Molar mass | 542.54441 | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Flocoumafen is an anticoagulant of the 4-hydroxycoumarin vitamin K antagonist type. It is a second generation (i.e., high potency) chemical in this class, used commercially as a rodenticide. It has a very high toxicity and is restricted to indoor use and sewers (in the UK). This restriction is mainly due to the increased risk to non-target species, especially due to its tendency to bio-accumulate in exposed organisms. Studies have shown that rodents resistant to first generation anticoagulants, can be adequately controlled with Flocoumafen.
References
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.