Fifth metatarsal bone
| Fifth metatarsal bone | |
|---|---|
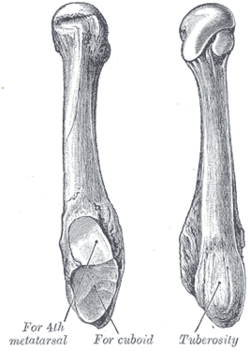 | |
| The fifth metatarsal. (Left.) | |
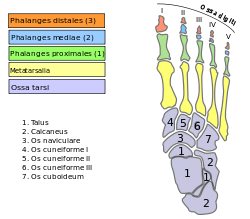 | |
| Bones of the right foot. Dorsal surface. Fifth metatarsal bone is the yellow bone farthest the right | |
| Latin | os metatarsale V |
| Gray's | p.274 |
| FMA | FMA:24506 |
The fifth metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot. It is the second smallest of the five metatarsal bones. The fifth metatarsal is analogous to the fifth metacarpal bone in the hand[1]
As with the four other metatarsal bones it can be divided into three parts; a base, body and head. The base is the part closest to the ankle and the head is closest to the toes. The narrowed part in the middle is referred to as the body (or shaft) of the bone. The bone is somewhat flat giving it two surfaces; the plantar (towards the sole of the foot) and the dorsal side (the area facing upwards while standing).[1] These surfaces are rough for the attachment of ligaments. The bone is curved longitudinally, so as to be concave below, slightly convex above.
The base articulates behind, by a triangular surface cut obliquely in a transverse direction, with the cuboid; and medially, with the fourth metatarsal. The fifth metatarsal has a rough eminence, the tuberosity, on the lateral side of its base. The plantar surface of the base is grooved for the tendon of the abductor digiti quinti.
The head articulates with the fifth proximal phalanx, the first bone in the fifth toe.
A strong band of the plantar aponeurosis connects the projecting part of the tuberosity with the lateral process of the tuberosity of the calcaneus.
The base of the metatarsal is often injured and a particularly notorious fracture is the Jones fracture. When the tuberosity is broken, it is called a pseudo-Jones fracture or a dancer's fracture.[2] This is a common fracture of the fifth metatarsal.[3] Stress fractures are common in the fifth metatarsal among athletes.
Muscle attachments
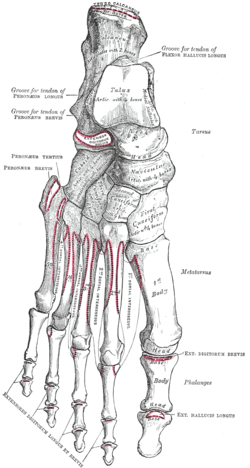 Muscle attachments (seen from above) | 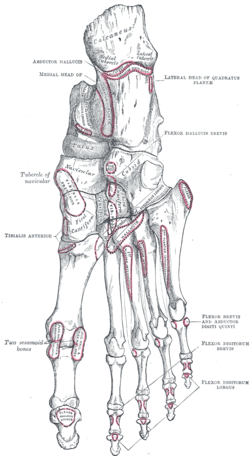 Muscle attachments (seen from below) |
The tendon of the fibularis tertius inserts on the medial part of the dorsal surface and the fibularis brevis on the dorsal surface of the tuberosity.
The plantar surface of the base is grooved for the tendon of the abductor digiti quinti, and gives origin to the flexor digiti minimi brevis.
The fourth dorsal interossei muscles originates from the medial side of shaft. The function of the muscle is to spread the toes.[4]
The third Plantar interossei muscle originates from the medial side of the base and shaft of the fifth metatarsal. The function of the muscle is to move the fourth toe medially and move the toes together.[4]
The horizontal head of the adductor hallucis from the deep transverse metatarsal ligament,[4] a narrow band which runs across and connects together the heads of all the metatarsal bones.
| Muscle | Direction | Attachment[5] |
| Fibularis tertius | Insertion | Dorsal side of the basis |
| Fibularis brevis | Insertion | Tuberosity |
| Flexor digiti minimi brevis | Origin | Plantar surface of the base |
| Dorsal interossei IV | Origin | Medial side of the shaft |
| Plantar interossei III | Origin | Medial side of the base and shaft |
| Horizontal head of adductor hallucis | Origin | Deep transverse metatarsal ligament |
Additional images
-

X-ray of foot, showing phalangeal fracture
-
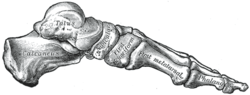
Skeleton of foot. Medial aspect.
-

Oblique section of left intertarsal and tarsometatarsal articulations, showing the synovial cavities.
-

Foot bones – tarsus, metatarsus
-

Foot bones – metatarsus and phalanges
-
Metatarsus
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Bojsen-Møller, Finn; Simonsen, Erik B.; Tranum-Jensen, Jørgen (2001). Bevægeapparatets anatomi [Anatomy of the Locomotive Apparatus] (in Danish) (12th ed.). p. 246. ISBN 978-87-628-0307-7.
- ↑ Robert Silbergleit. "Foot Fracture". Medscape.com. Retrieved 19 October 2011.
- ↑ Gary A. Rosenberg and James J. Sferra (September/October 2000). "Treatment Strategies for Acute Fractures and Nonunions of the Proximal Fifth Metatarsal". Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 8 (5): 332–338.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Bojsen-Møller, Finn; Simonsen, Erik B.; Tranum-Jensen, Jørgen (2001). Bevægeapparatets anatomi [Anatomy of the Locomotive Apparatus] (in Danish) (12th ed.). pp. 300–301. ISBN 978-87-628-0307-7.
- ↑ Bojsen-Møller, Finn; Simonsen, Erik B.; Tranum-Jensen, Jørgen (2001). Bevægeapparatets anatomi [Anatomy of the Locomotive Apparatus] (in Danish) (12th ed.). pp. 364–367. ISBN 978-87-628-0307-7.
This article incorporates text from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Fifth metatarsal bone. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||