Fibularis tertius
| Fibularis tertius | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Muscles of the front of the leg. (peroneus tertius visible at center left) | |
| Latin | Musculus peronaeus tertius, musculus fibularis tertius |
| Gray's | p.482 |
| Origin | distal anterior surface of the fibula |
| Insertion | dorsal surface of metatarsal 5 |
| Artery | anterior tibial artery |
| Nerve | deep fibular nerve |
| Actions | dorsiflexion and eversion of the foot |
The fibularis tertius (/ˌfɪbjʉˈlɛərɨs ˈtɛrʃi.əs/) (also known as peroneus tertius) is a muscle of the human body located in the lower limb.
The muscle arises from the lower third of the anterior surface of the fibula; from the lower part of the interosseous membrane; and from an intermuscular septum between it and the peroneus brevis muscle. The septum is sometimes called the intermuscular septum of Otto.
The tendon, after passing under the superior extensor retinaculum of foot and inferior extensor retinaculum of foot in the same canal as the extensor digitorum longus, is inserted into the dorsal surface of the base of the metatarsal bone of the fifth digit.
It is innervated by the deep fibular nerve, unlike the other peroneal muscles which are innervated by the superficial fibular nerve, since the peroneus tertius is a member of the anterior compartment.
Its action is that of weak dorsiflexion of the ankle joint and to evert the foot at the ankle joint.
This muscle is seldom found in other primates, a fact that has linked its function to efficient terrestrial bipedalism.
Gallery
-
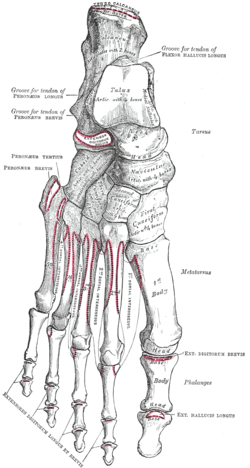
Bones of the right foot (dorsal surface).
-

The mucous sheaths of the tendons around the ankle (lateral aspect).
-
Dorsum of Foot. Deep dissection.
-
Dorsum of Foot. Deep dissection.
See also
External links
- LUC pert
- -1288372144 at GPnotebook
- 15:st-0411 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Leg: Muscles"
- Fibularis+tertius at eMedicine Dictionary
- PTCentral
This article incorporates text from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||