Fenamic acid
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Fenamic acid | ||
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| IUPAC name 2-(phenylamino)benzoic acid | ||
| Other names N-phenylanthranilic acid | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 91-40-7 | |
| PubChem | 4386 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:34756 | |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL23832 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 | |
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C13H11NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 213.23 g/mol | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Fenamic acid is a molecule which serves as a parent structure for several non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including mefenamic acid, tolfenamic acid, flufenamic acid, and meclofenamic acid.
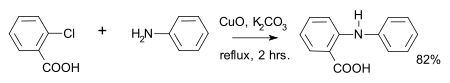
This compound may be synthesized by the reaction of 2-chlorobenzoic acid and aniline, with base and copper oxide catalyst in the Goldberg reaction.[1]
The self-condensation of fenamic acid yields acridone.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 C. F. H. Allen and G. H. W. McKee (1943), "Acridone", Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol. 2: 15
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.