Fandaqumiya
| Fandaqumiya | |
|---|---|
| Other transcription(s) | |
| • Arabic | الفندقومية |
| • Also spelled |
al-Fandaqumiya (official) Pentakomia (unofficial) |
 | |
 Fandaqumiya | |
| Coordinates: 32°19′13″N 35°12′13″E / 32.32028°N 35.20361°ECoordinates: 32°19′13″N 35°12′13″E / 32.32028°N 35.20361°E | |
| Governorate | Jenin |
| Government | |
| • Type | Village Council |
| Area | |
| • Jurisdiction | 3,895 dunams (3.9 km2 or 1.5 sq mi) |
| Population (2006) | |
| • Jurisdiction | 3,363 |
Fandaqumiya, (Arabic: الفندقومية, al-Fandaqumiyah, Pentakomia) is a Palestinian village located in the Jenin Governorate of the northern West Bank, northwest of Nablus. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics, the town had a population of 3,363 inhabitants in mid-year 2006.[1]
Name
The Arabic name of the village, Al Fandaqumiyah (الفندقومي), is a corruption of the Greek term Pentakomia: Komia means 'village' or 'community', while penta means 'five'. Pentakomia probably refers to an administrative unit of five villages which existed in the area.[2][3][4]
A Pentakomia in Greece[citation needed] as well as one on the Euphrates River[5] probably share the etymology, and the Hebron area village of Tarqumiyah (Arabic ترقوميا) is based on the Greek Trikomia, or 'community of three.'
Geography
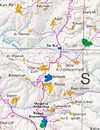
The village is in the northern West Bank, on the road leading north from Nablus to Jenin. It is located between the ancient ruins of Samaria and Sebaste and the Sanur Valley. It is also neighbored by the villages of Jaba and Silat ad-Dhahr, as well as the former settlements of Homesh and Sa-Nur, which were dismantled in Israel's unilateral disengagement plan.
History
Pre-Historic Period
The earliest findings in Fandaqumiya include a white clay jar filled with burned bones, which was found in a tomb. The examination of this jar at the Archaeological Department of the An-Najah National University suggested that it be dated to the Neolithic Period. A stone tool, circular in shape with a hole in the middle, was found alongside the jar, though it was never dated[citation needed].
Hellenistic Period
Two coins dating back to the Greek period were found in the village. A prutah minted by Hasmonean ruler Alexander Jannaeus between 103 and 76 BCE, as well as a Greek coin of the Ptolmaic dynasty dated to the year 300 BCE.
Roman, Byzantine, & Crusader Period
There is evidence that the village flourished during the Early Roman and Late Byzantine periods. Many Roman and Byzantine coins were discovered on site, and many tombs from the same period were found in a nearby hill. Additionally several structures characteristic of the Roman and Byzantine periods have been unearthed.
A sacred cave exists above the village on the south, which is probably an ancient rock-cut chapel.[6]
The village was mentioned in Crusader sources in 1178.[7]
The Ottoman Period
Several coins and structures, including a mosque, may date from the Mamluk period, however very little else is known about the site during that stage[citation needed].
In 1596 Fandaqumiyya appeared in the Ottoman tax registers as being in the nahiya of Jabal Sami in the liwa of Nablus. It had a population of 11 households and 1 bachelor, all Muslim. Taxes were paid on wheat, barley, summer crops, olive trees, occasional revenues, goats and beehives, and a press for olives or grapes.[8]
The modern settlement was renewed in 1820 when Ahmad Anbar and his family arrived from Hebron and were granted a homestead in the well-known ruin by the local ruler of the Sanur area, Haj Ahmad Jarrar[citation needed]. Because Haj Ahmad operated independent of the Ottomans, the Sanur fortress was besieged by the authorities around 1830, and many of the local villages were pillaged, including Fandaqumiya. While the population had fled during the hostilities, the village was eventually repaired and more families continued to arrive.
French explorer Victor Guérin visited the village in 1863 and 1870, and estimated it as having about 500 inhabitants. He describes it as being situated on the slopes of a high hill. With abundant waters, the whole slope was cultivated with beautiful olive trees, figs and pomegranates.[2] In The Survey of Western Palestine (1882), Fendakumiyeh was described as "a very small village on the slope of the hill, with three springs to the south-west, small and marshy."[4]
A spur of the Ottoman Hejaz railway to Damascus was built through the area, and a station was opened nearby at Sebastia. After the collapse of the Ottomans, locals took apart the rail infrastructure for secondary use in construction. Many of the steel beams can still be seen in the roofs of local homes.
British Mandate
In 1917, Fandaqumiya was captured by General Allenby's British forces from the Ottomans, and three years later it was assigned to the British Mandatory Palestine.
Soon after the British arrived, they built a police fort on a nearby hill. Despite many villagers being employed in the construction, relations with the British forces were at times rocky owing to tax disputes. During the riots of 1936-1939, some villagers launched attacks on the British troops, and the village was subject to British reprisals.
During the 1940s, the British administration funded modern water and agriculture development projects as well as an elementary school.
In the 1922 census of Palestine, conducted by the British Mandate authorities, Fandaqumiya had a population of 327, all Muslims.[9] This had increased in the 1931 census when El Fandaqumiya had 101 occupied houses and a population of 445, still all Muslim.[10] In 1945 the population was 630 Arabs, with 4,079 dunams of land, according to an official land and population survey.[11] 885 dunams were used for plantations and irrigable land, 2,737 dunams for cereals,[12] while 14 dunams were built-up (urban) land.[13]
The Modern Period
After the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, Fandaqumiya was ruled by the Hashemites of Jordan. Al Fandaqumiya passed to Israeli control along with the rest of the West Bank after the 1967 Six-Day War, though after the 1995 signing of the Interim Agreement on the West Bank and the Gaza Strip, it has been administered by the Palestinian Authority.
References
- ↑ Projected Mid -Year Population for Jenin Governorate by Locality 2004- 2006 Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Guérin, 1875, p. 216-217
- ↑ Palmer, 1881, p. 182
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Conder and Kitchener, 1882, vol 2, p. 155
- ↑ There is a locality of this name in Arabia
 "Pentacomia". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company. 1913.
"Pentacomia". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company. 1913. - ↑ Conder and Kitchener, 1882, vol 2, p. 185
- ↑ Rey, 1883, p. 426
- ↑ Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 125.
- ↑ Barron, 1923, Table IX, Sub-district of Jenin,
- ↑ Mills, 1932, p. 68
- ↑ Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. Village Statistics, April, 1945. Quoted in S. Hadawi, Village Statistics, 1945. PLO Research Center, 1970, p. 54
- ↑ Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. Village Statistics, April, 1945. Quoted in S. Hadawi, Village Statistics, 1945. PLO Research Center, 1970, p. 98
- ↑ Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. Village Statistics, April, 1945. Quoted in S. Hadawi, Village Statistics, 1945. PLO Research Center, 1970, p. 148
Bibliography
- Barron, J. B., ed. (1923). Palestine: Report and General Abstracts of the Census of 1922. Government of Palestine.
- Conder, Claude Reignier; Kitchener, H. H. (1882). The Survey of Western Palestine: Memoirs of the Topography, Orography, Hydrography, and Archaeology 2. London: Committee of the Palestine Exploration Fund.
- Guérin, Victor (1875). Description Géographique Historique et Archéologique de la Palestine (in French). 2: Samarie, pt. 2. Paris: L'Imprimerie Nationale.
- Hadawi, Sami (1970). Village Statistics of 1945: A Classification of Land and Area ownership in Palestine. Palestine Liberation Organization Research Center.
- Hütteroth, Wolf-Dieter; Abdulfattah, Kamal (1977). Historical Geography of Palestine, Transjordan and Southern Syria in the Late 16th Century. Erlanger Geographische Arbeiten, Sonderband 5. Erlangen, Germany: Vorstand der Fränkischen Geographischen Gesellschaft. ISBN 3-920405-41-2.
- E. Mills, ed. (1932). Census of Palestine 1931. Population of Villages, Towns and Administrative Areas. Jerusalem: Government of Palestine.
- Palmer, E. H. (1881). The Survey of Western Palestine: Arabic and English Name Lists Collected During the Survey by Lieutenants Conder and Kitchener, R. E. Transliterated and Explained by E.H. Palmer. Committee of the Palestine Exploration Fund.
- Rey, Emmanuel Guillaume (1883). Les colonies franques de Syrie aux XIIme et XIIIme siècles (in French). Paris: A. Picard.
External links
- Erection of a permanent military checkpoint and devastation of land inside the evacuated colony of Sanur, 12, May, 2007, ARIJ
- Welcome To al-Fandaqumiya
| |||||||||||||
