External jugular vein
| Vein: External jugular vein | |
|---|---|
 | |
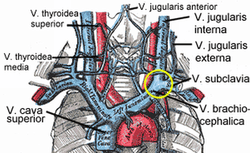
| Veins of the head and neck. (External jugular visible at center.) | |
 | |
| Veins | |
| Latin | vena jugularis externa |
| Gray's | p.646 |
| Drains from | cranium, face |
| Source | posterior facial vein, posterior auricular vein, anterior jugular vein |
| Drains to | subclavian vein |
| MeSH | Jugular+Veins |
The external jugular vein receives the greater part of the blood from the exterior of the cranium and the deep parts of the face, being formed by the junction of the posterior division of the retromandibular vein with the posterior auricular vein.
Path
It commences in the substance of the parotid gland, on a level with the angle of the mandible, and runs perpendicularly down the neck, in the direction of a line drawn from the angle of the mandible to the middle of the clavicle at the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoideus.
In its course it crosses the sternocleidomastoideus obliquely, and in the subclavian triangle perforates the deep fascia, and ends in the subclavian vein lateral to or in front of the scalenus anterior, piercing the roof of the posterior triangle.
It is separated from the sternocleidomastoideus by the investing layer of the deep cervical fascia, and is covered by the platysma, the superficial fascia, and the integument; it crosses the cutaneous cervical nerve, and its upper half runs parallel with the great auricular nerve.
The external jugular vein varies in size, bearing an inverse proportion to the other veins of the neck, it is occasionally double.
The external jugular vein drains into the subclavian vein lateral to the junction of the subclavian vein and the internal jugular vein.
Valves
It is provided with two pairs of valves, the lower pair being placed at its entrance into the subclavian vein, the upper in most cases about 4 cm above the clavicle. The portion of vein between the two sets of valves is often dilated, and is termed the sinus.
These valves do not prevent the regurgitation of the blood, or the passage of injection from below upward.[1]
Tributaries
This vein receives the occipital occasionally, the posterior external jugular, and, near its termination, the transverse cervical, transverse scapular, and anterior jugular veins; in the substance of the parotid, a large branch of communication from the internal jugular joins it.
Use In Medicine
The external jugular is a large vein used in prehospital medicine for venous access when the EMT is unable to find another peripheral vein. It is commonly used in cardiac arrest or other situations where the patient is unresponsive due to the pain associated with the procedure. In a cardiac arrest using this vein has the advantage that the paramedic can stay at the head and intubate the patient as well. Although many EMTs and paramedics use this vein the American Heart Association still recommends the use of the antecubital vein.
Additional images
-

External jugular vein
-

Muscles of the head, face, and neck.
-

Section of the neck at about the level of the sixth cervical vertebra.
-

Diagram showing completion of development of the parietal veins.
-

The veins of the neck, viewed from the front.
-
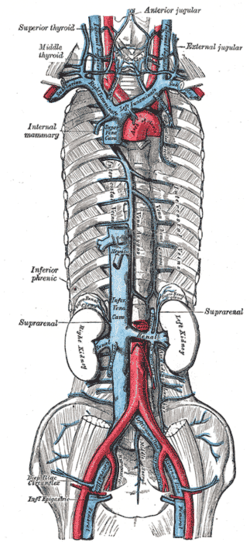
The venæ cavæ and azygos veins, with their tributaries.
-

Scheme showing relative positions of primary lymph sacs.
-
External jugular vein.Deep dissection.Lateral view.
See also
References
- ↑ Gray's Anatomy of the Human Body
External links
- lesson4 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (parotid2)
This article incorporates text from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
