Exeter point
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In geometry, the Exeter point is a special point associated with a plane triangle. The Exeter point is a triangle center and is designated as the center X(22)[1] in Clark Kimberling's Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers. This was discovered in a computers-in-mathematics workshop at Phillips Exeter Academy in 1986.[2] This is one of the recent triangle centers, having discovered only in 1986, unlike the classical triangle centers like centroid, incenter, and Steiner point.[3]
Definition
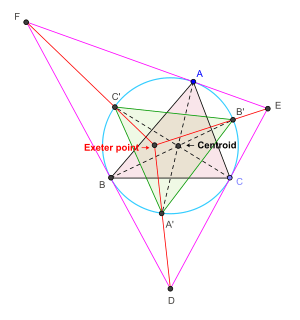
The Exeter point is defined as follows.[2][4]
- Let ABC be any given triangle. Let the medians through the vertices A, B, C meet the circumcircle of triangle ABC at A' , B' and C' respectively. Let DEF be the triangle formed by the tangents at A, B, and C to the circumcircle of triangle ABC. (Let D be the vertex opposite to the side formed by the tangent at the vertex A, E be the vertex opposite to the side formed by the tangent at the vertex B, and F be the vertex opposite to the side formed by the tangent at the vertex C.) The lines through DA' , EB' and FC' are concurrent. The point of concurrence is the Exeter point of triangle ABC.
Trilinear coordinates
The trilinear coordinates of the Exeter point are
- ( a ( b4 + c4 − a4 ), b ( c4 + a4 − b4 ), c ( a4 + b4 − c4 ) ).
Properties
- The Exeter point of triangle ABC lies on the Euler line (the line passing through the centroid, the orthocenter and the circumcenter) of triangle ABC.
See also
References
- ↑ Kimberling, Clark. "Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers: X(22)". Retrieved 24 May 2012.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Kimberling, Clark. "Exeter Point". Retrieved 24 May 2012.
- ↑ Kimberling, Clark. "Triangle centers". Retrieved 24 May 2012.
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W. "Exeter Point". From MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource. Retrieved 24 May 2012.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.