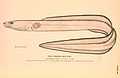
European conger
| European conger | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Anguilliformes |
| Family: | Congridae |
| Genus: | Conger |
| Species: | C. conger |
| Binomial name | |
| Conger conger (Linnaeus, 1758) | |
 | |
| The Range of the European conger | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The European conger, Conger conger, is a species of conger of the family Congridae. It is the largest eel in the world and native to the northeast Atlantic, including the Mediterranean Sea.
Description and behavior
European congers have a common length of 150 cm (59 in), a maximum length of 3 m (9.8 ft), and weigh up to 110 kg (240 lb), making them the largest eels in the world.
The body is very long, anguilliform, without scales. The color is usually gray but can also be blackish. The belly is white. A row of white small spots is aligned along the lateral line. The head is almost conical, slightly depressed. The snout is rounded and prominent, with lateral olfactory holes. The large gill openings are in lateral position. The conical teeth are arranged in rows on jaws. The dorsal and anal fins are confluent with caudal. Pectoral fins are present, while ventral fins are absent.

Distribution
This species can be found in the eastern Atlantic from Norway and Iceland to Senegal, and also in the Mediterranean and Black Sea.
Habitat
Conger conger ranges from 0-500 m of depth. It is sometimes seen in very shallow water by the shore, but can also go down to depths of 1,170 m (3,840 ft). It is usually present on rocky and sandy bottoms, close to the coast when young, moving to deeper waters when adult.
Gallery
References
- Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2006). "Conger conger" in FishBase. May 2006 version.
- Animal Base
- Boldsystems
- EoL
- ITIS
- WoRMS
- UNEP-WCMC Species Database
- Animal Diversity
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Conger conger. |
| Wikispecies has information related to: European conger |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||