Ethyl decanoate
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Ethyl decanoate | |
|---|---|
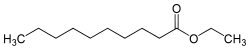 | |
| IUPAC name Ethyl decanoate | |
| Other names Ethyl caprate; Ethyl caprinate; Ethyl decylate; Capric acid ethyl ester; Decanoic acid ethyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 110-38-3 |
| PubChem | 8048 |
| ChemSpider | 7757 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C12H24O2 |
| Molar mass | 200.32 g mol−1 |
| Density | 0.862 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −26 °C; −15 °F; 247 K |
| Boiling point | 245 °C; 473 °F; 518 K |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Ethyl decanoate, also known as ethyl caprate, is a fatty acid ester formed from capric acid and ethanol. This ester is a frequent product of fermentation during winemaking, especially at temperatures above 15°C. [1]
References
- ↑ Killian, E.; Ough, C. S. (1979). "Fermentation Esters — Formation and Retention as Affected by Fermentation Temperature". American Journal of Enology and Viticulture 30 (4): 301–305.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.