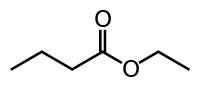
Ethyl butyrate
| Ethyl butyrate | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| IUPAC name Ethyl butanoate | |
| Other names Ethyl n-butanoate, Ethyl n-butyrate, Butanoic acid ethyl ester, Butyric acid ethyl ester, Butyric ether, UN 1180 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 105-54-4 |
| PubChem | 7762 |
| ChemSpider | 7475 |
| UNII | UFD2LZ005D |
| EC number | 203-306-4 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL44800 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties[1] | |
| Molecular formula | C6H12O2 |
| Molar mass | 116.16 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid with fruity odor (typically pineapple) |
| Density | 0.879 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −93 °C; −135 °F; 180 K |
| Boiling point | 120 to 121 °C; 248 to 250 °F; 393 to 394 K |
| Solubility in water | Soluble in 150 parts |
| Vapor pressure | 1510 Pa (11.3 mm Hg) |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | External MSDS |
| R-phrases | R10 R36/37/38 |
| S-phrases | S16 S26 S36 |
| Main hazards | Irritant (Xi) |
| NFPA 704 |
 2
1
0
|
| Flash point | 78 °F (26 °C) c.c. |
| Autoignition temperature | 463 °C; 865 °F; 736 K |
| LD50 | 13050 mg/kg (oral, rat)[1] |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Structure and properties |
n, εr, etc. |
| Thermodynamic data |
Phase behaviour Solid, liquid, gas |
| Spectral data | UV, IR, NMR, MS |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Ethyl butyrate, also known as ethyl butanoate, or butyric ether, is an ester with the chemical formula CH3CH2CH2COOCH2CH3. It is soluble in propylene glycol, paraffin oil, and kerosene. It has a fruity odor, similar to pineapple.[1]
Uses
It is commonly used as artificial flavoring resembling orange juice[2] or pineapple in alcoholic beverages (e.g. martinis, daiquiris etc.), as a solvent in perfumery products, and as a plasticizer for cellulose. In addition, ethyl butyrate is often also added to orange juice, as most associate its odor with that of fresh orange juice.
Ethyl butyrate is one of the most common chemicals used in flavors and fragrances. It can be used in a variety of flavors: orange (most common), cherry, pineapple, mango, guava, bubblegum, peach, apricot, fig, and plum. In industrial use, it is also one of the cheapest chemicals, which only adds to its popularity.
Production
It can be synthesized by reacting ethanol and butyric acid. This is a condensation reaction, meaning water is produced in the reaction as a byproduct.
See also
References
External links
- MSDS sheet
- Sorption of ethyl butyrate and octanal constituents of orange essence by polymeric adsorbents
- Biosynthesis of ethyl butyrate using immobilized lipase: a statistical approach