Erdős–Diophantine graph
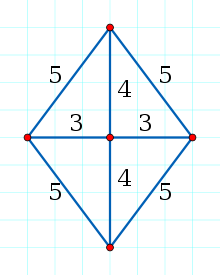
An Erdős–Diophantine graph is an object in the mathematical subject of Diophantine equations consisting of a set of integer points at integer distances in the plane that cannot be extended by any additional points. Equivalently,
it can be described as a complete graph with vertices located on the integer square grid 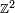 such that all mutual distances between the vertices are integers, while all other grid points have a non-integer distance to at least one vertex.
such that all mutual distances between the vertices are integers, while all other grid points have a non-integer distance to at least one vertex.
Erdős–Diophantine graphs are named after Paul Erdős and Diophantus of Alexandria. They form a subset of the set of Diophantine figures, which are defined as complete graphs in the Diophantine plane for which the length of all edges are integers. Thus, Erdős–Diophantine graphs are exactly the Diophantine figures that cannot be extended. The existence of Erdős–Diophantine graphs follows from the Erdős–Anning theorem, according to which infinite Diophantine figures must be collinear in the Diophantine plane. Hence, any process of extending a non-collinear Diophantine figure by adding vertices must eventually reach a figure that can no longer be extended.
Examples
Graphs with fewer than three nodes are always collinear, so Erdős–Diophantine graphs with fewer than three nodes cannot exist (since they can be trivially extended).
By numerical search, Kohnert and Kurz have shown that triangular Erdős–Diophantine graphs do exist. The smallest Erdős–Diophantine triangle is characterised by edge lengths 2066, 1803, and 505. The next larger Erdős–Diophantine triangle has edges 2549, 2307 and 1492. In both cases, the sum of the three edge-lengths is even. Brancheva has proven that this property holds for all Erdős–Diophantine triangles. More generally, the total length of any closed path in an Erdős–Diophantine graph is always even.
An example of a 4-node Erdős–Diophantine graph is provided by the complete graph formed by the four nodes located on the vertices of a rectangle with sides 4 and 3.
References
- Kohnert, Axel; Kurz, Sascha (2005). "A note on Erdős–Diophantine graphs and Diophantine carpets". arXiv:math/0511705 [math.CO]..
- Dimiev, Stancho; Markov, Krassimir (2002). "Gauss integers and Diophantine figures". arXiv:math/0203061 [math.NT]..