Eprosartan
 | |
|---|---|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
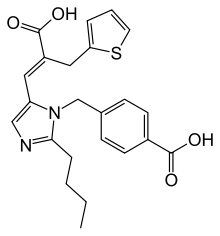
| 4-({2-Butyl-5-[2-carboxy-2-(thiophen-2-ylmethyl)eth-1-en-1-yl]-1H-imidazol-1-yl}methyl)benzoic acid | |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Teveten |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601237 |
| Legal status | ? |
| Routes | Oral |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 15% (Eprosartan mesylate) |
| Metabolism | not metabolized |
| Half-life | 5 to 9 hours |
| Excretion | Renal 10%, biliary 90% |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 133040-01-4 |
| ATC code | C09CA02 |
| PubChem | CID 5281037 |
| DrugBank | DB00876 |
| ChemSpider | 4444504 |
| UNII | 2KH13Z0S0Y |
| KEGG | D04040 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:4814 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL813 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C23H24N2O4S |
| Mol. mass | Eprosartan mesylate: 520.625 g/mol |
| SMILES
| |
| |
| | |
Eprosartan is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist used for the treatment of high blood pressure. It is marketed as Teveten by Abbvie in the United States.It is marketed as Eprozar by INTAS Pharmaceuticals in India and by Abbott Laboratories elsewhere. It is sometimes paired with hydrochlorothiazide, marketed in the US as Teveten HCT and elsewhere as Teveten Plus.
The drug acts on the renin-angiotensin system in two ways to decrease total peripheral resistance. First, it blocks the binding of angiotensin II to AT1 receptors in vascular smooth muscle, causing vascular dilatation. Second, it inhibits sympathetic norepinephrine production, further reducing blood pressure.
As with other angiotensin II receptor antagonists, eprosartan is generally better tolerated than enalapril (an ACE inhibitor), especially among the elderly.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ Ruilope L, Jäger B, Prichard B (2001). "Eprosartan versus enalapril in elderly patients with hypertension: a double-blind, randomized trial". Blood Press. 10 (4): 223–9. doi:10.1080/08037050152669747. PMID 11800061.
External links
| ||||||||||||||||||||