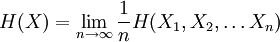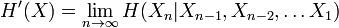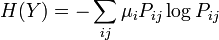Entropy rate
In the mathematical theory of probability, the entropy rate or source information rate of a stochastic process is, informally, the time density of the average information in a stochastic process. For stochastic processes with a countable index, the entropy rate H(X) is the limit of the joint entropy of n members of the process Xk divided by n, as n tends to infinity:
when the limit exists. An alternative, related quantity is:
For strongly stationary stochastic processes, 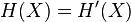 . The entropy rate can be thought of as a general property of stochastic sources; this is the asymptotic equipartition property.
. The entropy rate can be thought of as a general property of stochastic sources; this is the asymptotic equipartition property.
Entropy rates for Markov chains
Since a stochastic process defined by a Markov chain that is irreducible and aperiodic has a stationary distribution, the entropy rate is independent of the initial distribution.
For example, for such a Markov chain Yk defined on a countable number of states, given the transition matrix Pij, H(Y) is given by:
where μi is the stationary distribution of the chain.
A simple consequence of this definition is that the entropy rate of an i.i.d. stochastic process has an entropy rate that is the same as the entropy of any individual member of the process.
See also
References
- Cover, T. and Thomas, J. (1991) Elements of Information Theory, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., ISBN 0-471-06259-6
External links
- Systems Analysis, Modelling and Prediction (SAMP), University of Oxford MATLAB code for estimating information-theoretic quantities for stochastic processes.