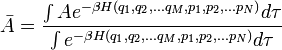Ensemble average
In statistical mechanics, the ensemble average is defined as the mean of a quantity that is a function of the micro-state of a system (the ensemble of possible states), according to the distribution of the system on its micro-states in this ensemble.
Since the ensemble average is dependent on the ensemble chosen, its mathematical expression varies from ensemble to ensemble. However, the mean obtained for a given physical quantity doesn't depend on the ensemble chosen at the thermodynamic limit.
Canonical ensemble average
Classical statistical mechanics
For a classical system in thermal equilibrium with its environment, the ensemble average takes the form of an integral over the phase space of the system:
- where:
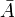 is the ensemble average of the system property A,
is the ensemble average of the system property A,
 is
is  , known as thermodynamic beta,
, known as thermodynamic beta,
- H is the Hamiltonian of the classical system in terms of the set of coordinates
 and their conjugate generalized momenta
and their conjugate generalized momenta  , and
, and
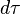 is the volume element of the classical phase space of interest.
is the volume element of the classical phase space of interest.
The denominator in this expression is known as the partition function, and is denoted by the letter Z.
Quantum statistical mechanics
For a quantum system in thermal equilibrium with its environment, the weighted average takes the form of a sum over quantum energy states, rather than a continuous integral:
Characterization of the classical limit
Ensemble average in other ensembles
The generalized version of the partition function provides the complete framework for working with ensemble averages in thermodynamics, information theory, statistical mechanics and quantum mechanics.