Enol ether
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
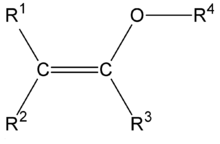
The structure of a typical enol ether group.
An enol ether is an alkene with an alkoxy substituent. The general structure is  with R an alkyl or an aryl group. Enol ethers and enamines are so-called activated alkenes or electron rich alkenes because the oxygen atom donates electrons to the double bond by forming a resonance structure with the corresponding oxonium ion. This property makes them reactive substrates in certain organic reactions such as the Diels-Alder reaction. An enol ether can be considered the ether of the corresponding enolate, hence the name. Two simple enol ethers are methyl vinyl ether and 2,3-dihydrofuran.
with R an alkyl or an aryl group. Enol ethers and enamines are so-called activated alkenes or electron rich alkenes because the oxygen atom donates electrons to the double bond by forming a resonance structure with the corresponding oxonium ion. This property makes them reactive substrates in certain organic reactions such as the Diels-Alder reaction. An enol ether can be considered the ether of the corresponding enolate, hence the name. Two simple enol ethers are methyl vinyl ether and 2,3-dihydrofuran.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.