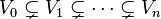Engel's theorem
In representation theory, a branch of mathematics, Engel's theorem is one of the basic theorems in the theory of Lie algebras; it asserts that for a Lie algebra two concepts of nilpotency are identical. A useful form of the theorem says that if a Lie algebra L of matrices consists of nilpotent matrices, then they can all be simultaneously brought to a strictly upper triangular form. The theorem is named after the mathematician Friedrich Engel, who sketched a proof of it in a letter to Wilhelm Killing dated 20 July 1890 (Hawkins 2000, p. 176). Engel's student K.A. Umlauf gave a complete proof in his 1891 dissertation, reprinted as (Umlauf 2010).
A linear operator T on a vector space V is defined to be nilpotent if there is a positive integer k such that Tk = 0. For example, any operator given by a matrix whose entries are zero on and below its diagonal is nilpotent.
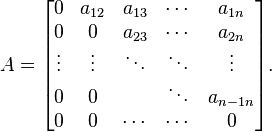
An element x of a Lie algebra L is ad-nilpotent if and only if the linear operator on L defined by
is nilpotent. Note that in the Lie algebra L(V) of linear operators on V, the identity operator IV is ad-nilpotent (because  ) but is not a nilpotent operator.
) but is not a nilpotent operator.
A Lie algebra L is nilpotent if and only if the lower central series defined recursively by
eventually reaches {0}.
Theorem. A finite-dimensional Lie algebra L is nilpotent if and only if every element of L is ad-nilpotent.
Note that no assumption on the underlying base field is required.
The key lemma in the proof of Engel's theorem is the following fact about Lie algebras of linear operators on finite dimensional vector spaces which is useful in its own right:
Let L be a Lie subalgebra of L(V). Then L consists of nilpotent operators if and only if there is a sequence
of subspaces of V such that 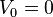 ,
, 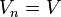 and
and
Thus Lie algebras of nilpotent operators are simultaneously strictly upper-triangulizable.
See also
- Lie's theorem
References
- Erdmann, Karin & Wildon, Mark. Introduction to Lie Algebras, 1st edition, Springer, 2006. ISBN 1-84628-040-0
- Hawkins, Thomas (2000), Emergence of the theory of Lie groups, Sources and Studies in the History of Mathematics and Physical Sciences, Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag, ISBN 978-0-387-98963-1, MR 1771134
- G. Hochschild, The Structure of Lie Groups, Holden Day, 1965.
- J. Humphreys, Introduction to Lie Algebras and Representation Theory, Springer, 1972.
- Umlauf, Karl Arthur (2010) [1891], Über Die Zusammensetzung Der Endlichen Continuierlichen Transformationsgruppen, Insbesondre Der Gruppen Vom Range Null, Inaugural-Dissertation, Leipzig (in German), Nabu Press, ISBN 978-1-141-58889-3
![\operatorname {ad}_{x}(y)=[x,y]\](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/4/6/b/3/46b343ddb9ff05e0fb5d54fb43ea337d.png)
![{\mathbf {L}}^{0}={\mathbf {L}},\quad {\mathbf {L}}^{{i+1}}=[{\mathbf {L}},{\mathbf {L}}^{i}]\](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/5/f/2/7/5f27b6ae2349c820c73d2216b17dacc3.png)