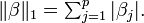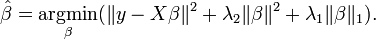Elastic net regularization
In statistics and, in particular, in the fitting of linear or logistic regression models, the elastic net is a regularized regression method that linearly combines the L1 and L2 penalties of the lasso and ridge methods.
Specification
The elastic net method overcomes the limitations of the LASSO (least absolute shrinkage and selection operator) method which uses a penalty function based on
Use of this penalty function has several limitations.[1] For example, in the "large p, small n" case (high dimensional data with few examples), the LASSO selects at most n variables before it saturates. Also if there is a group of highly correlated variables, then the LASSO tends to select one variable from a group and ignore the others. To overcome these limitations, the elastic net adds a quadratic part to the penalty ( ), which when used alone is ridge regression (known also as Tikhonov regularization). The estimates from the elastic net method are defined by
), which when used alone is ridge regression (known also as Tikhonov regularization). The estimates from the elastic net method are defined by
As a result, the elastic net method includes the LASSO and ridge regression: in other words, each of them is a special case where 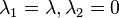 or
or 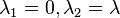 . Meanwhile, the naive version of elastic net method finds an estimator in a two-stage procedure : first for each fixed
. Meanwhile, the naive version of elastic net method finds an estimator in a two-stage procedure : first for each fixed 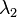 it finds the ridge regression coefficients, and then does a LASSO type shrinkage. This kind of estimation incurs a double amount of shrinkage, which introduces unnecessary extra bias and outcomes with bad prediction performance. To improve the prediction performance, the authors rescale the coefficients of the naive version of elastic net by multiplying the estimated coefficients by
it finds the ridge regression coefficients, and then does a LASSO type shrinkage. This kind of estimation incurs a double amount of shrinkage, which introduces unnecessary extra bias and outcomes with bad prediction performance. To improve the prediction performance, the authors rescale the coefficients of the naive version of elastic net by multiplying the estimated coefficients by 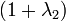 .[1]
.[1]
Software
- "Glmnet: Lasso and elastic-net regularized generalized linear models" is software which is implemented as an R source package.[2][3] This includes fast algorithms for estimation of generalized linear models with ℓ1 (the lasso), ℓ2 (ridge regression) and mixtures of the two penalties (the elastic net) using cyclical coordinate descent, computed along a regularization path.
- JMP Pro 11 includes elastic net regularization, using the Generalized Regression personality with Fit Model.
- "pensim: Simulation of high-dimensional data and parallelized repeated penalized regression" implements an alternate, parallelised "2D" tuning method of the ℓ parameters, a method claimed to result in improved prediction accuracy.[4][5]
- scikit-learn includes linear regression, logistic regression and linear support vector machines with elastic net regularization.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Zou, Hui; Hastie, Trevor (2005). "Regularization and Variable Selection via the Elastic Net". Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B: 301–320.
- ↑ Friedman, Jerome; Trevor Hastie and Rob Tibshirani (2010). "Regularization Paths for Generalized Linear Models via Coordinate Descent". Journal of Statistical Software: 1–22.
- ↑ http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/glmnet/index.html
- ↑ Waldron, L.; Pintilie, M.; Tsao, M. -S.; Shepherd, F. A.; Huttenhower, C.; Jurisica, I. (2011). "Optimized application of penalized regression methods to diverse genomic data". Bioinformatics 27 (24): 3399–3406. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btr591. PMC 3232376. PMID 22156367.
- ↑ http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/pensim/index.html