El Khiam
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
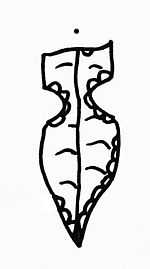
El Khiam Point - first found at El Khiam
| El Khiam | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | Israel |
| Coordinates | 31°38′00″N 35°15′00″E / 31.633333°N 35.25°E |
| History | |
| Periods | Mesolithic, Neolithic |
| Cultures | Khiamian |
| Site notes | |
| Excavation dates | 1931, 1957, 1961 |
| Archaeologists | R. Neuville, André Parrot, González Echergaray |
| Public access | Unknown |
El Khiam is an archaeological site near Wadi Khureitun in the Judean desert in Israel, on the shores of the Dead Sea.
Archaeological finds at el-Khiam show nearly continuous habitation by groups of hunters since the Mesolithic and early Neolithic periods.[1] The Khiamian (c. 10000-9500 BC.) period, named for this site, is characterized by flint arrowheads now known as "El Khiam Points."[2]
El Khiam was first excavated by R. Neuville in 1934, by André Parrot in 1951 and González Echergaray in 1961.[2]
References
Further reading
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.