Edward Walter Maunder
| Edward Walter Maunder | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born |
12 April 1851 London |
| Died | 21 March 1928 (aged 76) |
| Nationality | British |
| Fields | astronomy |
| Known for | Maunder Minimum |
| Spouse |
Edith Hannah Bustin (1875–1888) Annie Scott Dill Russell (1895–1928) |
Edward Walter Maunder (12 April 1851 – 21 March 1928) was an English astronomer best remembered for his study of sunspots and the solar magnetic cycle that led to his identification of the period from 1645 to 1715 that is now known as the Maunder Minimum.
Early and personal life
Edward Walter Maunder was born in 1851, in London, the youngest child of a minister of the Wesleyan Society. He attended King's College London but never graduated. He took a job in a London bank to finance his studies.
In 1873 Maunder returned to the Royal Observatory, taking a position as a spectroscopic assistant. Shortly after, in 1875, he married Edith Hannah Bustin, who gave birth to six children, 3 sons, 2 daughters and a son who died in infancy.[1] Following the death of Edith in 1888, he met Annie Scott Dill Russell (1868–1947) in 1890, a mathematician and astronomer with whom he collaborated for the remainder of his life. In 1895 Maunder and Russell married. In 1916 Annie Maunder became one of the first women accepted by the Royal Astronomical Society.
Solar observations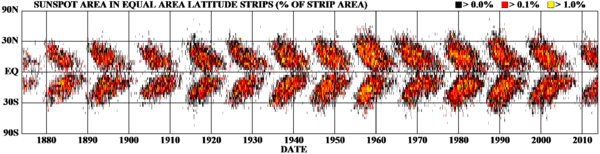
Part of Maunder's job at the Observatory involved photographing and measuring sunspots, and in doing so he observed that the solar latitudes at which sunspots occur varies in a regular way over the course of the 11 year cycle. After 1891, he was assisted in his work by his second wife, Annie Scott Dill Maunder (née Russell), a mathematician educated at Girton College in Cambridge. She worked as a "lady computer" at the Observatory from 1890 to 1895. In 1904, he published their results in the form of the "butterfly" diagram.
After studying the work of Gustav Spörer, who examined old records from the different observatories archives looking for changes of the heliographic latitude of sunspots, Maunder announced Spörer's conclusions in own paper edited in 1894. The period, recognized earlier by Spörer, now bears Maunder's name.
He travelled extensively for observations going to places such as the West Indies, Lapland, India, Algiers, Mauritius. His last eclipse expedition was to Labrador for the Solar eclipse of August 30, 1905 at the invitation of the Canadian government.[2]
Other astronomical observations

In 1882 Maunder (and some other European astronomers) observed what he called an "auroral beam"; as yet unexplained, it had some similarity in appearance to either a noctilucent cloud or an upper tangent arc.[3] However, Maunder wrote that the phenomenon moved rapidly from horizon to horizon, which would rule out a noctilucent cloud or upper tangent arc. Further, upper tangent arc cannot occur during nighttime when the observation was made. Since he made his observation during highly intense auroral activity, he assumed it was some extraordinary auroral phenomenon, though one he had never observed again before or after.
He observed Mars and was a sceptic of the notion of Martian canals. He conducted visual experiments using marked circular disks which led him to conclude, correctly, that the viewing of canals arose as an optical illusion. Also he was convinced that there cannot be life "as in our world" on Mars, as there are no temperature-equating winds and too low mean temperatures. Craters on Mars and the Moon were named in his and his wife Annie's honour.
Establishment of the British Astronomical Association
In 1890, Maunder was a driving force in the foundation of the British Astronomical Association. Although he had been fellow of the Royal Astronomical Society since 1875, Maunder wanted an association of astronomers open to every person interested in astronomy, from every class of society, and especially open for women.
Maunder was the first editor of the Journal of the BAA, an office later taken by his wife Annie Maunder. His older brother, Thomas Frid Maunder (1841–1935), was a co-founder and secretary of the Association for 38 years.
Publications
- Maunder, E. Walter (1899). The Indian Eclipse, 1898: Report of the Expeditions Organized by the British Astronomical Association .... London: Hazel, Watson, and Viney, Ld. Retrieved 2008-04-17.
- Maunder, E. Walter (1900). The Royal Observatory, Greenwich—Original publication: London: The Religious Tract Society
- Maunder, E. Walter (1904). Astronomy without a Telescope. London: W. Thacker and Co. Retrieved 2008-04-17.
- Maunder, E. W. (1904). "Note on the Distribution of Sun-Spots in Heliographic Latitude, 1874-1902". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 64: 747–761. Bibcode:1904MNRAS..64..747M.
- Maunder, E. (1908, reprinted in 2007). Astronomy of the Bible: An Elementary Commentary on the Astronomical References in the Holy Scripture. New York: Mitchell Kennerley.
- Maunder, A. and E. (1910). The Heavens and their Story. London: Charles H. Kelly.
- Maunder, E. Walter (1912). The Science of the Stars. London: T.C. and E.C. Jack.
- Maunder, E. Walter (1913). Are the Planets Inhabited?. New York: Harper and Brothers. Retrieved 2008-04-17.
References
- ↑ "Obituary Notices: Fellows:- Maunder, Edward Walter". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 89: 313. February 1929. Bibcode:[http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1929MNRAS..89..313. 1929MNRAS..89..313.]
- ↑ Crommelin, A.C.D. (May 1928). "Obituary: Edward Walter Maunder". The Observatory 51: 157-159. Bibcode:1928Obs....51..157C.
- ↑ "Upper Tangent Arc". Arbeitskreis Meteore e.V.
Further reading
- Willie Wei-Hock Soon and Steven H. Yaskell: The Maunder Minimum and the Variable Sun-Earth Connection, World Scientific, 2003, ISBN 981-238-274-7
- Hector Macpherson (1905). Astronomers of To-day and Their Work. Gall & Inglis. by Hector Macpherson, London: Gall & Inglis, 1905
- A. J. Kinder "Edward Walter Maunder His Life and Times" Journal of the British Astronomical Association" Vol. 118 (1) 21-42 (2008).
External links
| Wikiquote has a collection of quotations related to: Edward Walter Maunder |
- Online catalogue of Maunder's personal and working papers (part of the Royal Greenwich Observatory Archive held at Cambridge University Library)
- J. E. Evans and E. W. Maunder, "Experiments as to the Actuality of the 'Canals' observed on Mars", MNRAS, 63 (1903) 488
- Drawing of the butterfly plot
|