Ecobank
 | |
| Type |
Public Company GSE: ETI NSE: ETIT BRVM: ETI |
|---|---|
| Industry | Financial Services |
| Founded | 1985 |
| Headquarters | 2365, Boulevard du Mono, B.P.3261, Lomé, Togo[1] |
| Key people |
André Siaka[2] Interim Chairman Thierry Tanoh Group CEO |
| Products | Banking Services, Investments, Funds Transfer, Products and Services including pan-African Lending, Trade Services, Cash Management, Internet Banking, Value-chain Finance, Treasury Services, Corporate Finance, Investment Banking and Securities and Asset Management |
| Revenue |
|
| Total assets | US$ 20.0 billion (2012) |
| Employees | 18,698 (2013) |
| Website | Homepage |
Ecobank, whose official name is Ecobank Transnational Inc. (ETI), but is also known as Ecobank Transnational, is a pan-African banking conglomerate, with banking operations in 33 African countries. It is the leading independent regional banking group in West Africa and Central Africa, serving wholesale and retail customers. It also maintains subsidiaries in Eastern Africa, as well as in Southern Africa. ETI has representative offices in Angola, China, Dubai, France, South Africa and in the United Kingdom.
Overview
ETI is a large financial services provider with offices in 37 countries around the world, and presence in 33 sub-Saharan countries. As of December 2012, ETI's customer base was estimated at 13.7 million, with 9.6 million (70.2%), located in Nigeria, the continent's most populous nation. At that time, the group's total assets were valued at US$20.0 billion, with shareholders' equity of US$2.176 billion.[4] ETI's branch network numbered 1,251, with 1,981 networked ATMs. The bank had 18,698 employees, in 37 countries, in Africa, Asia and Europe, at the end of May 2013.
Group network
As of October 2013, Ecobank Transnational had banking operations in 35 African countries, with representative offices in Angola, Beijing, Dubai, Ethiopia, South Africa and the United Kingdom:[5]
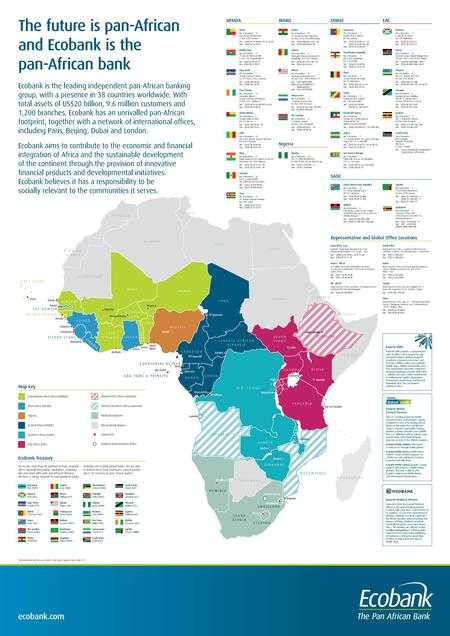
Ecobank Transnational has operational bank subsidiaries in the following countries, as of July 2013:
- Africa
- Ecoboank Angola - (Representative office in Luanda)
- Ecobank Benin
- Ecobank Burkina Faso
- Ecobank Burundi
- Ecobank Cameroon
- Ecobank Cape Verde
- Ecobank Central African Republic
- Ecobank Chad
- Ecobank Congo Brazzaville
- Ecobank Côte d'Ivoire
- Ecobank Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Ecobank Ethiopia - (Representative office in Addis Ababa)
- Ecobank Equatorial Guinea
- Ecobank Gabon
- Ecobank Gambia
- Ecobank Ghana
- Ecobank Guinea
- Ecobank Guinea-Bissau
- Ecobank Kenya
- Ecobank Liberia
- Ecobank Malawi
- Ecobank Mali
- Ecobank Niger
- Ecobank Nigeria (includes Oceanic Bank)[6]
- Ecobank Rwanda
- Ecobank São Tomé and Príncipe
- Ecobank Senegal
- Ecobank Sierra Leone
- Ecobank South Africa (Representative office in Johannesburg)
- Ecobank South Sudan[7]
- Ecobank Tanzania [8]
- Ecobank Togo
- Ecobank Uganda
- Ecobank Zambia[9]
- Ecobank Zimbabwe
- Outside Africa
- Paris, France - Affiliate office
- London, United Kingdom - France affiliate representative office
- Dubai, United Arab Emirates - Representative office
- Beijing, China - Representative office
History
ETI, a public limited liability company, was established as a bank holding company in 1985 under a private sector initiative spearheaded by the Federation of West African Chambers of Commerce and Industry, with the support of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS). In the early 1980s the banking industry in West Africa was dominated by foreign and state-owned banks. There were hardly any commercial banks in West Africa owned and managed by the African private sector. ETI was founded with the objective of filling this vacuum.
The Federation of West African Chambers of Commerce promoted and initiated a project for the creation of a private regional banking institution in West Africa. In 1984, Ecopromotions S.A. was incorporated. Its founding shareholders raised the seed capital for the feasibility studies and the promotional activities leading to the creation of ETI.
In October 1985, ETI was incorporated with an authorised capital of US$100 million. The initial paid up capital of US$32 million was raised from over 1,500 individuals and institutions from West African countries. The largest shareholder was the ECOWAS Fund for Cooperation, Compensation and Development (ECOWAS Fund), the development finance arm of ECOWAS. A Headquarters’ Agreement was signed with the government of Togo in 1985 which granted ETI the status of an international organisation with the rights and privileges necessary for it to operate as a regional institution, including the status of a non-resident financial institution.
ETI has two specialised subsidiaries: Ecobank Development Corporation (EDC) and eProcess International (eProcess). EDC was incorporated with a broad mandate to develop Ecobank’s investment banking and advisory businesses throughout the countries where Ecobank operates. EDC operates brokerage houses on all 3 stock exchanges in West Africa and has obtained licences to operate on the two stock exchanges in Central Africa: the Douala Stock Exchange in Cameroon and the Libreville Exchange in Gabon. The mandate of eProcess is to manage the Group’s information technology function with a view to ultimately centralising the Group’s middle and back office operations to improve efficiency, service standards and reduce costs.[10]|
Subsidiaries
The Specialized subsidiary companies of Ecobank include the following: [11]
- EBI SA Groupe Ecobank - Paris, France
- EBI SA Representative Office - London, United Kingdom
- Ecobank Development Corporation (EDC) - Lomé, Togo
- EDC Investment Corporation - Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire
- EDC Investment Corporation - Douala, Cameroon
- EDC Securities Limited - Lagos, Nigeria
- EDC Stockbrokers Limited - Accra, Ghana
- Ecobank Asset Management - Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire
- e-Process International SA - Lomé, Togo
- Ecobank Asset Management Company P/L - Harare, Zimbabwe
The Ecobank Nedbank alliance
With more than 1,500 branches in 35 countries, the Ecobank-Nedbank Alliance is the largest banking network in Africa. The alliance was formed in 2008 between the Ecobank Group and the Nedbank Group, one of South Africa's four largest financial services providers, with a growing footprint of operations across the Southern African Development Community. [12]
Ownership
The shares of Ecobank Transnational Inc., the parent company of Ecobank, are traded on three West African stock exchanges, namely: the Ghana Stock Exchange (GSE), the Nigeria Stock Exchange (NSE) and the BRVM stock exchange in Abidjan, Ivory Coast. [13] As of December 2012, the ten largest institutional shareholders in Ecobank Transnational are listed in the table below: [14]
| Rank | Shareholder | Percentage Ownership |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | STD NOMS TVL PTY LTD/RENAISSANCE DIRECT INVST | 18.69 |
| 2 | Ecowas Bank for Investment & Development (BIDC) | 6.21 |
| 3 | Social Security and National Insurance Trust (SSNIT) | 5.53 |
| 4 | Interlink Securities Limited | 4.86 |
| 5 | AFRICA INVST SUB 1 LTD | 4.41 |
| 6 | Bourse Regionale des Valeurs Mobilieres (BRVM) | 4.20 |
| 7 | IICMG SEC (STRUCTURED) | 3.36 |
| 8 | Blakeney Group III Limited | 2.61 |
| 9 | GLG/HSBC-TRADING | 2.36 |
| 10 | Metropolitan Trust Nigeria Limited | 1.72 |
See also
- Ecobank Ghana
- Ecobank Nigeria
- Ecobank Uganda
- Ecobank Zimbabwe
External links
- Ecobank official site
- (French) Ecobank official site
- Ecobank Transnational Incorporated at Nigerian Stock Exchange
- Ecobank Nigeria at Nigerian Stock Exchange
- (English) Modern Ghana, article 'Ecobank Takes over BICA in CAR'
- "Ecobank Bank Plc 2007 annual report". African Financials.
- Company Profile At Bloomberg.com
References
- ↑ Company Headquarters in Lome, Togo
- ↑ Kolapo Lawson Hands Over To Andre Siaka As Interim Chairman
- ↑ December 2012 Financial Data
- ↑ December 2012 Financial Highlights
- ↑ Ecobank Increases Sub-Saharan Africa Offices To 35
- ↑ Oceanic Bank Acquired By Ecobank Transnational
- ↑ Ecobank Opens In South Sudan
- ↑ Ecobank Opening in Tanzania in January 2010
- ↑ Ecobank Zambia Established In 2009
- ↑ History of Ecobank Transnational Inc.
- ↑ Ecobank Specialized Subsidiaries
- ↑ About The Ecobank-Nedbank Alliance
- ↑ Ecobank Investment Matters
- ↑ Shareholding In Ecobank Transnational
| ||||||||||||||