Duchy of Brunswick
| Duchy of Brunswick Herzogtum Braunschweig | ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
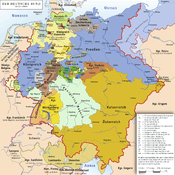
 Location of the Duchy of Brunswick within the German Empire | ||||||
| Capital | Braunschweig | |||||
| Government | Absolute monarchy | |||||
| Duke | ||||||
| - | 1813–15 (first) | Frederick William | ||||
| - | 1913–18 (last) | Ernest Augustus | ||||
| Historical era | Modern era | |||||
| - | Restoration | 1815 | ||||
| - | Abdication | 1918 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | 1910 | 3,672 km² (1,418 sq mi) | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | 1910 est. | 494,339 | ||||
| Density | 134.6 /km² (348.7 /sq mi) | |||||
The Duchy of Brunswick (German: Herzogtum Braunschweig) was a historical state in Germany. Its capital was the city of Brunswick (Braunschweig). It was established as the successor state of the Principality of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel by the Congress of Vienna in 1815. In the course of the 19th-century history of Germany, the duchy was part of the German Confederation, the North German Confederation and from 1871 the German Empire. It was disestablished after the end of World War I, its territory incorporated into the Weimar Republic as the Free State of Brunswick.
Duchy of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel
The title "Duke of Brunswick and Lüneburg" (German: Herzog zu Braunschweig und Lüneburg) was held, from 1235 on, by various members of the Welf family who ruled several small territories in northwest Germany. These holdings did not have all of the formal characteristics of a state, being neither compact nor indivisible. When several sons of a Duke competed for power, the lands were often divided between them; when a branch of the family lost power or became extinct, the lands were reallocated among surviving members of the family; different dukes might also exchange territories. The unifying element of all these territories was that they were ruled by male-line descendants of Duke Otto I.
After several early divisions, Brunswick-Lüneburg was unified under Duke Magnus II (d. 1373). Following his death, his three sons jointly ruled the Duchy. After the murder of their brother Frederick of Brunswick-Lüneburg, brothers Bernard and Henry redivided the land, Henry receiving the territory of Wolfenbüttel.
House of Brunswick
- Albert the Tall 1269–1279. Received southern half of Brunswick-Lüneburg as Prince of Wolfenbüttel while his brother John became Prince of Lüneburg. Albert's sons first ruled jointly, but in 1291 divided the Wolfenbüttel territory:
- Henry the Admirable became Prince of Grubenhagen 1291–1322
- Albert II the Fat became Prince of Göttingen 1286–1318
- William received Wolfenbüttel proper but died in 1292. Wolfenbüttel fell to his brother Albert II.
- Otto the Mild 1318–1344, son of Albert II, was Prince of Wolfenbüttel and Prince of Göttingen. After his death his son
- Ernest became Prince of Göttingen 1344–1367.
- Magnus the Pious became Prince of Wolfenbüttel 1344–1369. Magnus' son
- Magnus II with the Necklace, Prince of Wolfenbüttel 1369–1373, claimed the Principality of Lüneburg against Albert of Saxe-Wittenberg. The Lüneburg War of Succession continued until 1388.
- Frederick 1373–1400, son of Magnus II, conquered Lüneburg in 1388. Succeeded by his brothers:
- Henry the Mild, 1400–1408
- Bernard, 1409–1428. Returned control of Wolfenbüttel to his nephew, Henry's son.
- William the Victorious 1428–1432, nephew. Was deprived by his brother:
- Henry the Peaceful 1432–1473, moved the residence to Wolfenbüttel.
- William the Victorious 1473–1482, again. William regained control of Wolfenbüttel after his brother's death, and left the Principality to his two sons:
- Frederick 1482–1484. Imprisoned and deprived of power by his younger brother:
- William IV 1484–1491. Took control of all of Wolfenbüttel, then ceded Wolfenbüttel to his sons. Died 1495.
- Co-rulers, sons of William IV:
- Henry V 1514–1568. Son of Henry IV. Converted to Lutheranism.
- Julius 1568–1589. Son of Henry V. Acquired Calenberg in 1584 on the death of his cousin Eric II.
- Henry Julius 1589–1613, son.
- Frederick Ulrich 1613–1634, son. Last of the male-descendants of Albert the Tall.
House of Dannenberg
On Frederick Ulrich's death, his complex of territories passed to a line of distant cousins ruling in Lüneburg. Wolfenbüttel was eventually awarded to Augustus, son of Henry of Dannenberg.
- Augustus 1635–1666
- Augustus's sons succeeded him, sometimes ruling together:
- Rudolph Augustus 1666–1704
- Anthony Ulrich 1685–1702, 1704–1714. Disputed with Hanover. Deposed 1702–1704 for allying with France in the War of the Spanish Succession. Converted to Catholicism 1709.
- Anthony Ulrich's sons succeeded him in sequence:
- Augustus William 1714–1731
- Louis Rudolph 1731–1735
House of Brunswick-Bevern
- Ferdinand Albert March–September 1735. Grandson of Augustus the Younger.
- Charles I 1735–1780. Son of Ferdinand Albert. Moved the ducal court from Wolfenbüttel to Braunschweig in 1753.
- Charles William Ferdinand 1780–1806. Son of Charles I. Died in battle at Jena.
- Frederick William 1806–1807, 1813–1815. Son of Charles William Ferdinand. From 1806 to 1813, Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel was occupied by France in the Napoleonic Wars. Died in battle at Quatre Bras.
Frederick William's son Charles (a minor at the time of his father's death) became the first Duke of independent Brunswick.
Duchy of Brunswick

History
Formal sovereignty confirmed
The territory of Wolfenbüttel was recognized as a sovereign state by the Congress of Vienna in 1815. It had been a portion of the medieval Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg. From 1705 onward, all other portions of Brunswick-Lüneburg except Wolfenbüttel had been held by the Prince of Calenberg and Celle, i.e. the Elector of Hanover, but the Wolfenbüttel line retained its independence from Hanover.
The Wolfenbüttel principality had for the period from 1807 to 1813 been held as part of the Kingdom of Westphalia. The Congress turned it into an independent country under the name Duchy of Brunswick.
Charles II (1815–1830)
The underage Duke Charles, the eldest son of Duke Frederick William (who had been killed in action), was put under the guardianship of George IV, the Prince Regent of the United Kingdom and Hanover.
First, the young duke had a dispute over the date of his majority. Then, in 1827, Charles declared some of the laws made during his minority invalid, which caused conflicts. After the German Confederation intervened, Charles was forced to accept those laws. His administration was considered corrupt and misguided.
In the aftermath of the July Revolution in 1830, Charles finally had to abdicate. The palace in Brunswick was completely destroyed.
William VIII (1830–1884)
When Charles' brother William VIII arrived in Brunswick on 10 September, he was received joyfully by the people. William originally considered himself only his brother's regent, but after a year declared himself ruling duke. Charles made several desperate attempts, unsuccessfully, to depose his brother.
William left most government business to his ministers, and spent most of his time outside of his state at his possessions in Oels.
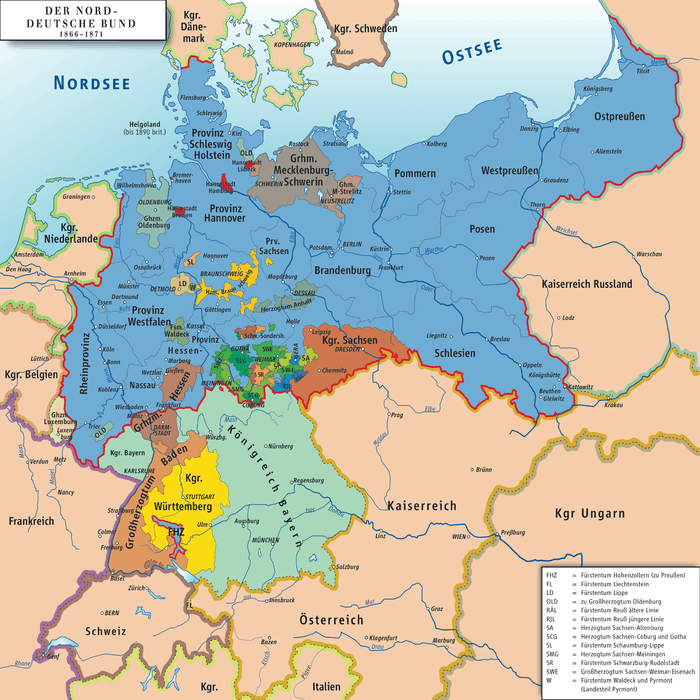
While William joined the Prussian-led North German Confederation in 1866, his relationship to Prussia was strained, since Prussia refused to recognize Ernest Augustus II of Hanover, 3rd Duke of Cumberland, his nearest male-line relative, as his heir.
While the Kingdom of Hanover was annexed by Prussia in 1866, the Duchy of Brunswick remained sovereign and independent. It joined first the North German Confederation and in 1871 the German Empire.
In the 1870s, it became obvious that the then senior branch of the ruling House of Welf would die with Duke William. By house law, the House of Hanover would have ascended the ducal throne. However, the Hanoverians still refused to accept the Prussian annexation of their kingdom. As a result, there was strong Prussian pressure against having George V of Hanover or his son, the Duke of Cumberland, succeed to Brunswick without severe conditions, including swearing allegiance to the German constitution and renouncing all claim to Hanover.
By a law of 1879, the Duchy of Brunswick established a temporary council of regency to take over at the Duke's death, and if necessary appoint a regent if the Duke of Cumberland were unable to succeed. With William's death in 1884, the Wolfenbüttel line came to an end. The Duke of Cumberland then proclaimed himself Duke of Brunswick. However, since he still claimed to be the rightful King of Hanover, the Federal Council ruled that he would violate the peace of the German Empire if he succeeded to Brunswick. Lengthy negotiations ensued, but were never resolved.
Regency (1884–1913)
Two regents were appointed: first, Prince Albert of Prussia until his death in 1906, and then Duke John Albert of Mecklenburg.
Ernest Augustus III (1913–1918)
The need for a Regent ended in 1913. The Duke of Cumberland's eldest son having died in 1912, the elderly Duke renounced Brunswick in favor of his youngest son, Ernest Augustus, who married Emperor Wilhelm II's daughter, swore allegiance to the German Empire, and renounced all claims to Hanover. Accordingly, he was allowed to ascend the throne of the Duchy in November 1913.
In the midst of the German revolutions of 1918, the Duke had to abdicate, and the Free State of Brunswick was founded as a member state of the Weimar Republic.
Dukes and Regents of Brunswick
House of Brunswick-Dannenberg
- 1815–1830: Charles II, son of Frederick William. Forced to flee Brunswick in 1830 and succeeded by his brother.
- 1830–1884: William VIII. Brother of Charles II. Last of the Brunswick line, following which the legal succession passed to the Hanoverian royal family, which had been dispossessed by Prussia following the Austro-Prussian War of 1866.
Regency
- 1885–1906: Albert, Prince of Prussia, regent. The German government prevented the succession of the Hanoverian Duke of Cumberland to the throne of Brunswick and substituted a Prussian regent for the Duke.
- 1907–1913: Duke Johann Albrecht of Mecklenburg-Schwerin, regent
House of Hanover
- 1913–1918: Ernest Augustus
Claimants to the Duchy
- Ernest Augustus, 3rd Duke of Cumberland (1884–1913), renounced
- the aforementioned Ernest Augustus III, the deposed duke of Brunswick (1918–1953), son of the previous
- Ernest Augustus the elder, Prince of Hanover (1953–1987)
- Ernest Augustus the younger, Prince of Hanover (1987–present)
For further information on the governments of Brunswick from 1918 on, see Free State of Brunswick.
Districts
The Duchy of Brunswick was subdivided into districts (Kreise) in 1833. The following districts existed from 1833 to 1946:
- District of Blankenburg (former County of Blankenburg): Blankenburg, Hasselfelde and Walkenried
- City of Braunschweig
- District of Braunschweig: Braunschweig, Riddagshausen and Vechelde
- District of Gandersheim: Gandersheim, Seesen, Lutter am Barenberge and Greene
- District of Goslar (from 1885 on)
- District of Helmstedt: Helmstedt, Schöningen, Königslutter, Vorsfelde and Calvörde
- District of Holzminden (until 1942): Holzminden, Stadtoldendorf, Ottenstein and Thedinghausen
- City of Watenstedt-Salzgitter (from 1942 on)
- District of Wolfenbüttel: Wolfenbüttel, Salder, Schöppenstedt and Harzburg.
Coat of arms

The duchy of Brunswick was formed out of the possessions of senior branch of the house of Brunswick. The house of Brunswick originated in Othbert Count Palatine of Este in Italy. This family acquired the inheritance of the Guelph family by marriage — around the year 1000 — of Azzo II with Kunigunde, daughter of Welf II. Again important possessions were gained in (Lower-)Saxony by the marriage of Henry 'the Black' to Wulfhild (d 1126), last of the Billung-family who had been dukes of Saxony for the last ages. They were made lord of Brunswick and Lüneburg in 1181 and dukes of Brunswick-Lüneburg on 12 August 1235. In 1546 the house of Brunswick-Lüneburg divided into the branches of Lüneburg (principality of Hanover) and Wolfenbüttel (the duchy of Brunswick).
Both branches used in their arms the two lions of Brunswick (said to be granted by the English king to his son in law, the duke of Brunswick in the thirteenth century), the blue lion of Lüneburg and the white horse of Saxony. The white horse is said to be the emblem of the eighth century Saxon duke Widukind after he and his barons were forcebly baptized by Charlemagne. Before he would have flown a black horse on a yellow cloth.
The standard of the dukes of Brunswick given by Siebmachers Wappenbuch, Nurenberg 1878, shows the white horse on a red cloth. The flag was blue over yellow, and demonstrates a remarkable similarity with the Ukrainian national colours.
The branch of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel died out however with Duke William on 18 October 1884. Brunswick and Hanover should have been rejoined at that time, but Prussia had annexed the kingdom of Hanover in 1866 and now prevented the younger branch of the house of Brunswick from taking up the ducal crown. Only in 1913 was peace sealed with the marriage of prince Ernest Augustus of Hanover to Victoria Louise, daughter of the German emperor William II. This couple was enthroned in the duchy of Brunswick. The flag they adopted shows however very much the English pattern in its form and contents. In the first and fourth quarter are the two lions of Brunswick, in the second and third the lion of Lüneburg. In the centre are the arms of Hanover (which are still on those of Great Britain!) now with a ducal crown. (source: Bulgaria Berühmte Fahnen Deutscher geschichte, Dresden 1922, p 61). To this day the princes of Hanover also are titled 'Prince(ss) of Great Britain and Ireland, Duke of Brunswick and Lüneburg'. This is not a valid style under British law, however, as no application has been made to restore the titles removed by the Titles Deprivation Act, 1917.
See also
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Brunswick (German duchy). |
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Duchy of Brunswick. |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||

.png)