DuPhos

Other phosphine asymmetric ligands were known at the time (DIPAMP, BINOL, CHIRAPHOS) but the new ligand was found to be more effective.
Description
The ligand consists of two 2,5-alkyl-substituted phospholane rings (the phosphorus analog of THF) connected via a 1,2-phenyl bridge. The alkyl group can be methyl, ethyl, propyl or isopropyl. In the closely related bis(dimethylphospholano)ethane or BPE ligand [3][4] the phenyl bridge is replaced by an 1,2-ethyl bridge. Both compounds can be obtained from the corresponding chiral diol through conversion to the cyclic sulfate and reaction with lithiated phenylbisphosphine. In DuPhos the phosphorus atoms are electron-rich making the resulting metal complexes reactive. The phosphorus atoms also introduce a kind of pseudo-chirality making enantioselection independent of the overall chemical conformation [5]
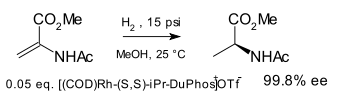
Another early application is the synthesis of unnatural chiral amino acids in a formal reductive amination [6] for example starting from benzophenone and the hydrazone of benzoyl chloride:[7]
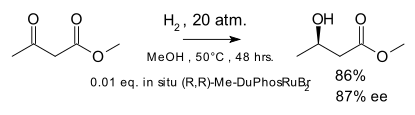
In the original scope the metal catalyst was rhodium but catalysis by ruthenium was introduced in 1995 [8] with the hydrogenation of the ketone group in β-keto esters:
Applications
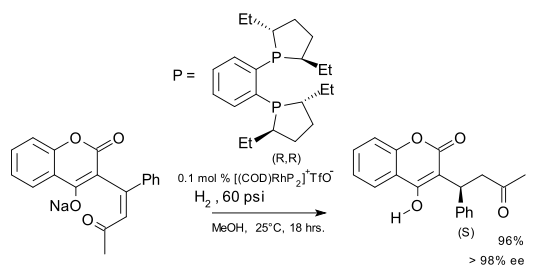
An application of an asymmetric synthesis with a DuPhos ligand is the hydrogenation of dehydrowarfarin to warfarin:[9]
Duphos is also applied in the synthesis of tryptophan derivatives.[10]
In polymerization catalysis
DuPhos ligands are used in metal catalyzed alpha-olefin / carbon monoxide copolymerization to form chiral isotactic polyketones. The first publication in this field dates back to 1994 with catalyst system [Pd(Me-DuPhos(MeCN)2)](BF4)2 [11]
BozPhos ligand
Mono oxidation of (R,R)-Me-Duphos using borane dimethylsulfide as protective group and hydrogen peroxide as oxidizing agent gives bozPhos [12][13] This ligand is useful in copper-catalyzed asymmetric addition of diorganozinc reagents to N-diphenylphosphinoylimines.
References
- ↑ C2-symmetric bis(phospholanes) and their use in highly enantioselective hydrogenation reactions Mark J. Burk J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1991, 113 (22), pp 8518–8519 doi:10.1021/ja00022a047
- ↑ Preparation and use of C2-symmetric bis(phospholanes): production of .alpha.-amino acid derivatives via highly enantioselective hydrogenation reactions Mark J. Burk, John E. Feaster, William A. Nugent, Richard L. Harlow J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1993, 115 (22), pp 10125–10138 doi:10.1021/ja00075a031
- ↑ New electron-rich chiral phosphines for asymmetric catalysis Mark J. Burk, John E. Feaster, Richard L. Harlow Organometallics, 1990, 9 (10), pp 2653–2655 doi:10.1021/om00160a010
- ↑ New chiral phospholanes; Synthesis, characterization, and use in asymmetric hydrogenation reactions Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, Volume 2, Issue 7, 1991, Pages 569-592 Mark J. Burk, John E. Feaster, Richard L. Harlow doi:10.1016/S0957-4166(00)86109-1
- ↑ Recent Developments in Catalytic Asymmetric Hydrogenation Employing P-Chirogenic Diphosphine Ligands Karen V. L. Crépy, Tsuneo Imamoto Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis Volume 345 Issue 1-2, Pages 79 - 101 2003 doi:10.1002/adsc.200390031
- ↑ Enantioselective hydrogenation of the C:N group: a catalytic asymmetric reductive amination procedure Mark J. Burk, John E. Feaster J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1992, 114 (15), pp 6266–6267 doi:10.1021/ja00041a067
- ↑ Catalytic asymmetric reductive amination of ketones via highly enantioselective hydrogenation of the C=N double bond Mark J. Burk , Jose P. Martinez, John E. Feaster and Nick Cosford Tetrahedron Volume 50, Issue 15, 11 April 1994, Pages 4399-4428 doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)89375-3
- ↑ Practical asymmetric hydrogenation of β-keto esters at atmospheric pressure using chiral Ru (II) catalysts J. P. Genêt, V. Ratovelomanana-Vidal, M. C. Caño de Andrade, X. Pfister, P. Guerreiro and J. Y. Lenoir Tetrahedron Letters Volume 36, Issue 27, 3 July 1995, Pages 4801-4804 doi:10.1016/0040-4039(95)00873-B
- ↑ The first practical asymmetric synthesis of R and S-Warfarin Andrea Robinson and Hui-Yin Li John Feaster Tetrahedron Letters Volume 37, Issue 46, 11 November 1996, Pages 8321-8324 doi:10.1016/0040-4039(96)01796-0
- ↑ A highly enantioselective asymmetric hydrogenation route to β-(2R,3S)-methyltryptophan R. Scott Hoerrner, David Askin, R.P. Volante and Paul J. Reider Tetrahedron Letters Volume 39, Issue 21, 21 May 1998, Pages 3455-3458 doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(98)00604-2
- ↑ Palladium(II)-Catalyzed Isospecific Alternating Copolymerization of Aliphatic .alpha.-Olefins with Carbon Monoxide and Isospecific Alternating Isomerization Cooligomerization of a 1,2-Disubstituted Olefin with Carbon Monoxide. Synthesis of Novel, Optically Active, Isotactic 1,4- and 1,5-Polyketones Zhaozhong Jiang, Ayusman Sen J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1995, 117 (16), pp 4455–4467 doi:10.1021/ja00121a003
- ↑ Alexandre Côté, Jean-Nicolas Desrosiers, Alessandro A. Boezio, and André B. Charette (2006), "Preparation of enantiomerically pure (R,R)-BozPhos", Org. Synth. 83: 1
- ↑ Jean-Nicolas Desrosiers, Alexandre Côté, Alessandro A. Boezio, and André B. Charette (2006), "Preparation of enantiomerically enriched (1S)-1-Phenylpropan-1-amine hydrochloride by a catalytic addition of diorganozinc reagents to imines", Org. Synth. 83: 5