Dopexamine
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
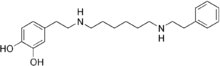 | |
|---|---|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| 4-[2-({6-[(2-phenylethyl)amino]hexyl}amino)ethyl]benzene-1,2-diol | |
| Clinical data | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Legal status | ? |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 86197-47-9 |
| ATC code | C01CA14 |
| PubChem | CID 55483 |
| ChemSpider | 50102 |
| UNII | 398E7Z7JB5 |
| KEGG | D03891 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL77622 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C22H32N2O2 |
| Mol. mass | 429.43 g/mol |
| SMILES
| |
| |
| | |
Dopexamine is a synthetic analogue of dopamine. Despite this, it is a β1 and β2-adrenergic receptor agonist.[1] Its action at dopamine receptor D1 mediates relaxation of vascular smooth muscle in renal, mesenteric, cerebral and coronary arteries. Mild action at D2 receptors decreases noradrenaline release.[2]
Use in sepsis has been proposed.[3]
It is used as an inotropic agent in cardiac failure.[4] Side effects include arrhythmia, tremor, angina and flushing.
References
- ↑ Perrin G, Papazian L, Martin C. (1993). "Dopexamine: a new dopaminergic agonist". Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 12 (3): 308–320. PMID 7902685.
- ↑ Brown RA, Dixon J, Farmer JB, et al. (July 1985). "Dopexamine: a novel agonist at peripheral dopamine receptors and beta 2-adrenoceptors". Br. J. Pharmacol. 85 (3): 599–608. PMC 1916510. PMID 2862944.
- ↑ Birnbaum J, Klotz E, Spies CD, et al. (2006). "Effects of dopexamine on the intestinal microvascular blood flow and leucocyte activation in a sepsis model in rats". Crit Care 10 (4): R117. doi:10.1186/cc5011. PMC 1750974. PMID 16893450.
- ↑ Lisbon A (May 2003). "Dopexamine, dobutamine, and dopamine increase splanchnic blood flow: what is the evidence?". Chest 123 (5 Suppl): 460S–3S. doi:10.1378/chest.123.5_suppl.460S. PMID 12740229.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.