Disodium phosphate
| Disodium phosphate | |
|---|---|
 | |
| IUPAC name Sodium hydrogen phosphate | |
| Other names Disodium hydrogen orthophosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 7558-79-4 10028-24-7 (dihydrate) 7782-85-6 (heptahydrate) 10039-32-4 (dodecahydrate) |
| PubChem | 24203 |
| ChemSpider | 22625 |
| UNII | 22ADO53M6F |
| EC number | 231-448-7 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:34683 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1060 |
| RTECS number | WC4500000 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:[Na+].[Na+].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | Na2HPO4 |
| Molar mass | 141.96 g/mol (anhydrous) 268.07 g/mol (heptahydrate) |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 1.7 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 250 °C decomp. |
| Solubility in water | 7.7 g/100 ml (20 °C) 11.8 g/100 mL (25 °C, heptahydrate) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 12.35 |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | ICSC 1129 |
| EU Index | Not listed |
| Main hazards | Irritant |
| NFPA 704 |
 0
1
0
|
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | sodium phosphite |
| Other cations | Dipotassium phosphate Diammonium phosphate |
| Related compounds | Monosodium phosphate Trisodium phosphate |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Disodium hydrogen phosphate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2HPO4. It is one of several sodium phosphates. The salt is known in anhydrous form as well as forms with 2, 7, 8, and 12 hydrates. All are water-soluble white powders; the anhydrous salt being hygroscopic.[1]
Acid-base properties
The pH of disodium hydrogen phosphate water solution is between 8.0 and 11.0, meaning it is basic:
- HPO42- + H2O
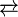 H2PO4- + OH-
H2PO4- + OH-
Production and reactions
It can be generated by neutralization of phosphoric acid with sodium hydroxide:
- H3PO42- + 2 NaOH → HNa2PO4 + 2 H2O
Industrially It is prepared in a two-step process by treating dicalcium phosphate with phosphoric acid, which precipitates calcium sulfate:[2]
- CaHPO4 + NaHSO4 → NaH2PO4 + CaSO4
In the second step, the resulting solution of monosodium phosphate is partially neutralized:
- NaH2PO4 + NaOH → HNa2PO4 + H2O
Uses
It is used as an in conjunction with trisodium phosphate in foods and water treatment. In foods, it is used to adjust pH. Its presence prevents coagulation in the preparation of condensed milk. Similarly, it is used as an anti-caking additive in powdered products.[3] It is used in desserts and puddings, e.g. Cream of Wheat to quicken cook time, and Jell-O Instant Pudding for thickening. In water treatment, It retards calcium scale formation. It is also found in some detergents and cleaning agents.[2]
Heating solid disodium phosphate gives the useful compound tetrasodium pyrophosphate:
- 2 HNa2PO4 → Na4P2O7 + H2O
Monobasic and dibasic sodium phosphate are used as a saline laxative to treat constipation or to clean the bowel before a colonoscopy.[4]
References
- ↑ Physical data (pdf)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Klaus Schrödter, Gerhard Bettermann, Thomas Staffel, Friedrich Wahl, Thomas Klein, Thomas Hofmann "Phosphoric Acid and Phosphates" in Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2008, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_465.pub3
- ↑ MSDS
- ↑
| ||||||||