Diplolaemus leopardinus
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Diplolaemus leopardinus | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Sauropsida |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Lacertilia |
| Family: | Leiosauridae |
| Genus: | Diplolaemus |
| Species: | D. leopardinus |
| Binomial name | |
| Diplolaemus leopardinus Werner, 1898 | |
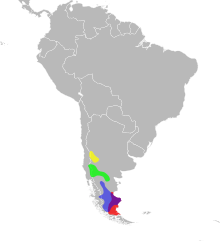 | |
| Red = D. darwinii Yellow = D. leopardinus Green = D. sextinctus Blue = D. bibronii | |
Diplolaemus leopardinus, commonly known as the leopard iguana or the leopard grumbler, is a species of lizard native to the southern tip of South America. It is found in the Patagonian Desert in the Araucania Region of Chile.
Description
The leopard iguana has a broad, triangular head and strong jaws. It is a medium-brown colour with bands of darker brown blotches. Its snout-to vent length is 5 to 9 cm (2.0 to 3.5 in). Its diet mostly consists of insects and other small invertebrates. It is found in the Lonquimay Valley, in the Araucanía Region of Chile, at elevations between 1,000 and 2,000 m (3,281 and 6,562 ft).[1]
References
- ↑ Chester, Sharon (2010). A Wildlife Guide to Chile: Continental Chile, Chilean Antarctica, Easter Island, Juan Fernandez Archipelago. Princeton University Press. p. 114. ISBN 9781400831500.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.