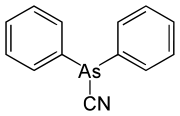
Diphenylcyanoarsine
| Diphenylcyanoarsine | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Diphenylarsinous cyanide | |
| Systematic name Diphenylarsanecarbonitrile | |
| Other names Clark 2 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 23525-22-6 |
| PubChem | 64506 |
| ChemSpider | 58070 |
| EC number | 245-716-6 |
| MeSH | Clark+2 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:C1=CC=C(C=C1)[As](C#N)C2=CC=CC=C2N#C[As](C1=CC=CC=C1)C1=CC=CC=C1|Image 1 Image 2 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C13H10AsN |
| Molar mass | 255.15 g mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Diphenylcyanoarsine, also called Clark 2 (Chlor-Arsen-Kampfstoff 2, being the successor of Clark 1) by the Germans, was discovered in 1918 by Sturniolo and Bellinzoni[1] and shortly thereafter used like the related Clark 1 gas by the Germans for chemical warfare in the First World War. The substance forms colourless, garlic-smelling crystals and causes nausea, vomiting and headaches. It can subsequently lead to e.g. pulmonary oedema (fluid on the lungs).
See also
- Clark 1
- Clark 3
- Chemical weapons
References
- ↑ Sturniolo, G. und Bellinzoni , G. (1919); Boll. chim. pharm., 58, 409–410