Diphenyl oxalate
| Diphenyl oxalate | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| IUPAC name diphenyl oxalate | |
| Other names diphenylethandioate, oxalic acid diphenyl ester, cyalume, DPO | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 3155-16-6 |
| PubChem | 18475 |
| ChemSpider | 17449 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C14H10O4 |
| Molar mass | 242.227 g/mol |
| Appearance | solid |
| Melting point | 136 °C; 277 °F; 409 K |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
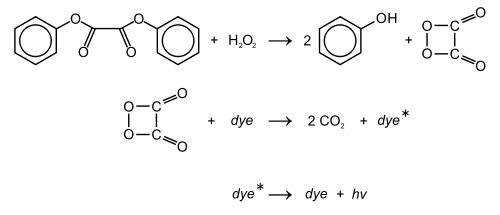
Diphenyl oxalate (trademark name Cyalume) is a solid ester whose oxidation products are responsible for the chemiluminescence in a glowstick. It can be synthesized by fully esterifying phenol with oxalic acid. The reaction with hydrogen peroxide that diphenyl oxalate undergoes produces phenol and 1,2-dioxetanedione, which excites the dye and releases a photon as it decomposes to carbon dioxide.
The reaction rate is pH dependent, and slightly alkaline conditions achieved by adding a weak base, e.g., sodium salicylate, will produce brighter light. The 2,4,6-trichlorophenol ester of oxalic acid is a solid and thus easier to handle. Furthermore, since trichlorophenolate is the better leaving group, the reaction will proceed faster, again producing brighter light, as compared to the phenol ester.
The following colors can be produced by using different dyes:
| Color | Compound |
|---|---|
| Blue | 9,10-Diphenylanthracene |
| Green | 9,10-Bis(phenylethynyl)anthracene |
| Yellow-green | Tetracene |
| Yellow | 1-Chloro-9,10-bis(phenylethynyl)anthracene |
| Orange | 5,12-Bis(phenylethynyl)naphthacene, Rubrene, Rhodamine 6G |
| Red | Rhodamine B |