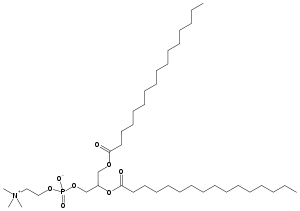
Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine
| Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 2644-64-6 |
| PubChem | 6138 |
| ChemSpider | 398235 |
| UNII | 2W15RT5V7V |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:O=C(OC[C@@H](OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC)COP([O-])(=O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C40H80NO8P |
| Molar mass | 734.039 g/mol |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPtdCho) is a phospholipid (and a lecithin) consisting of two palmitic acids and is the major constituent of pulmonary surfactant. It is also the only surface active component of lung surfactant capable of lowering surface tension to near zero levels. DPPtdCho is synthesized mainly through remodeling of phosphatidylcholine.
It is thought that a lysophosphatidylcholine (lysoPC) acyltransferase may play a critical role in its synthesis. The identity of this acyltransferase has not yet been confirmed.[1] Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine is an exception to the rule of thumb that biological phospholipids are synthesized with a saturated fat at the R1 position and an unsaturated fat at the R2 position.
It is also used for research purposes in studying liposomes, lipid bilayers, and model biological membranes and in the formation of reconstituted HDL (rHDL) particles.
See also
- Lecithin
- Colfosceril palmitate
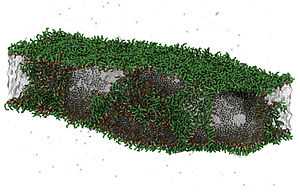
- Molecular Dynamics simulation of DPPC lipid bilayer formation in two phase systems
References
- ↑ Chen, Xueni; Hyatt, BA; Mucenski, ML; Mason, RJ; Shannon, JM (2006). "Identification and characterization of a lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase in alveolar type II cells". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103 (31): 11724–11729. doi:10.1073/pnas.0604946103. PMC 1544237. PMID 16864775.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DPPC molecule is zwitteronic having a negative charge on the phosphate group and a positive charge on the amine