Dinoxanthin
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Dinoxanthin | |
|---|---|
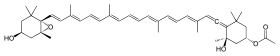 | |
| IUPAC name (3S,3'S,5R,5'R,6S)-3,5'-Dihydroxy-6',7'-didehydro-5,5',6,6'-tetrahydro-5,6-epoxy-β,β-caroten-3'-yl acetate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 54369-12-9 |
| PubChem | 16061289 |
| ChemSpider | 4947063 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:C[C@@]13O[C@]1(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C=C(C)/C=C/C=C(C)/[C@@H]=C=C2C(C)(C)C[C@@H](OC(C)=O)C[C@]2(C)O)C(C)(C)C[C@H](O)C3|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C42H58O5 |
| Molar mass | 642.91 g mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Dinoxanthin is a pigment found in dinoflagellates.[1][2] This compound is a potential antioxidant and may help to protect dinoflagellates against reactive oxygen species.[3]
References
- ↑ Loeblich AR, 3rd; Smith, VE (January 1968). "Chloroplast pigments of the marine dinoflagellateGyrodinium resplendens.". Lipids 3 (1): 5–13. doi:10.1007/BF02530961. PMID 17805834.
- ↑ Venn, AA; Wilson, MA; Trapido-Rosenthal, HG; Keely, BJ; Douglas, AE (December 2006). "The impact of coral bleaching on the pigment profile of the symbiotic alga, Symbiodinium.". Plant, cell & environment 29 (12): 2133–42. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2006.001587.x. PMID 17081247.
- ↑ Gallardo Rodríguez, JJ; Sánchez Mirón, A; García Camacho, F; Cerón García, MC; Belarbi, EH; Chisti, Y; Molina Grima, E (2009 May-Jun). "Causes of shear sensitivity of the toxic dinoflagellate Protoceratium reticulatum.". Biotechnology progress 25 (3): 792–800. doi:10.1002/btpr.161. PMID 19399843.
| |||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.