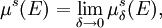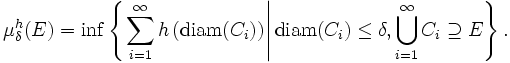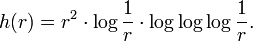Dimension function
In mathematics, the notion of an (exact) dimension function (also known as a gauge function) is a tool in the study of fractals and other subsets of metric spaces. Dimension functions are a generalisation of the simple "diameter to the dimension" power law used in the construction of s-dimensional Hausdorff measure.
Motivation: s-dimensional Hausdorff measure
Consider a metric space (X, d) and a subset E of X. Given a number s ≥ 0, the s-dimensional Hausdorff measure of E, denoted μs(E), is defined by
where
μδs(E) can be thought of as an approximation to the "true" s-dimensional area/volume of E given by calculating the minimal s-dimensional area/volume of a covering of E by sets of diameter at most δ.
As a function of increasing s, μs(E) is non-increasing. In fact, for all values of s, except possibly one, Hs(E) is either 0 or +∞; this exceptional value is called the Hausdorff dimension of E, here denoted dimH(E). Intuitively speaking, μs(E) = +∞ for s < dimH(E) for the same reason as the 1-dimensional linear length of a 2-dimensional disc in the Euclidean plane is +∞; likewise, μs(E) = 0 for s > dimH(E) for the same reason as the 3-dimensional volume of a disc in the Euclidean plane is zero.
The idea of a dimension function is to use different functions of diameter than just diam(C)s for some s, and to look for the same property of the Hausdorff measure being finite and non-zero.
Definition
Let (X, d) be a metric space and E ⊆ X. Let h : [0, +∞) → [0, +∞] be a function. Define μh(E) by
where
Then h is called an (exact) dimension function (or gauge function) for E if μh(E) is finite and strictly positive. There are many conventions as to the properties that h should have: Rogers (1998), for example, requires that h should be monotonically increasing for t ≥ 0, strictly positive for t > 0, and continuous on the right for all t ≥ 0.
Packing dimension
Packing dimension is constructed in a very similar way to Hausdorff dimension, except that one "packs" E from inside with pairwise disjoint balls of diameter at most δ. Just as before, one can consider functions h : [0, +∞) → [0, +∞] more general than h(δ) = δs and call h an exact dimension function for E if the h-packing measure of E is finite and strictly positive.
Example
Almost surely, a sample path X of Brownian motion in the Euclidean plane has Hausdorff dimension equal to 2, but the 2-dimensional Hausdorff measure μ2(X) is zero. The exact dimension function h is given by the logarithmic correction
I.e., with probability one, 0 < μh(X) < +∞ for a Brownian path X in R2. For Brownian motion in Euclidean n-space Rn with n ≥ 3, the exact dimension function is
References
- Olsen, L. (2003). "The exact Hausdorff dimension functions of some Cantor sets". Nonlinearity 16 (3): 963–970. doi:10.1088/0951-7715/16/3/309.
- Rogers, C. A. (1998). Hausdorff measures. Cambridge Mathematical Library (Third ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. xxx+195. ISBN 0-521-62491-6.