Dihydromorin
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Dihydromorin | ||
|---|---|---|
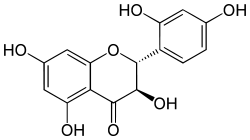 | ||
| IUPAC name (2R,3R)-2-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-2,3-dihydrochromen-4-one | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 18422-83-8 | |
| PubChem | 5458714 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 | |
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C15H12O7 | |
| Molar mass | 304.25 g/mol | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Dihydromorin is a flavanonol, a type of flavonoid. It can be found in plants of the family Moraceae including Morus nigra (Black mulberry),[1] in Morus alba,[2] Maclura pomifera (Maclura aurantiaca or Osage-Orange),[2] in the jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus)[3] and in Artocarpus dadah.[4]
Dihydromorin is an inhibitor of tyrosinase.[3]
See also
- Norartocarpetin, the corresponding flavone
References
- ↑ Black mulberry on naturalstandard.com
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Dihydromorin on liberherbarum.com
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Zheng, Zong-Ping; Chen, Sibao; Wang, Shiyun; Wang, Xia-Chang; Cheng, Ka-Wing; Wu, Jia-Jun; Yang, Dajiang; Wang, Mingfu (2009). "Chemical Components and Tyrosinase Inhibitors from the Twigs of Artocarpus heterophyllus". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 57 (15): 6649–55. doi:10.1021/jf9014685. PMID 19588925.
- ↑ Su, BN; Cuendet, M; Hawthorne, ME; Kardono, LB; Riswan, S; Fong, HH; Mehta, RG; Pezzuto, JM et al. (2002). "Constituents of the bark and twigs of Artocarpus dadah with cyclooxygenase inhibitory activity". Journal of Natural Products 65 (2): 163–9. doi:10.1021/np010451c. PMID 11858749.
| |||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.