Dihydromethysticin
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Dihydromethysticin | ||
|---|---|---|
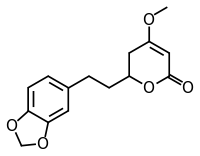 | ||
| IUPAC name (2S)-2-[2-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)ethyl]-4-methoxy-2,3-dihydropyran-6-one | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 19902-91-1 | |
| PubChem | 88308 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 | |
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C15H16O5 | |
| Molar mass | 276.28 g/mol | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Dihydromethysticin is one of the six major kavalactones found in the kava plant.[1]
Pharmacology
Dihydromethysticin has marked activity on the induction of CYP3A23, as does the related chemical desmethoxyyangonin.[2]
Both dihydromethysticin and methysticin induce the hepatic enzyme CYP1A1, which increases the amount of the very highly carcinogenic BP-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide in the body (via the metabolism of benzo(a)pyrene) and may be responsible for some of the toxic effects associated with kava consumption.
Dihydromethysticin possesses analgesic, anticonvulsant, and anxiolytic effects.[3]
pyrene_metabolism.svg.png)
Metabolism of benzo[a]pyrene yielding the carcinogenic benzo[a]pyren-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide.
References
- ↑ Malani, Joji (2002-12-03). "Evaluation of the effects of Kava on the Liver". Fiji School of Medicine. Retrieved 2009-09-04.
- ↑ Ma, Yuzhong; Karuna Sachdeva, Jirong Liu1, Michael Ford, Dongfang Yang, Ikhlas Khan, Clinton Chichester, Bingfang Yan (November 2004). "Desmethoxyyangonin and dihydromethysticin are two major pharmacological kavalactones with marked activity on the induction of CYP3A23.". Drug Metabolism and Disposition 32 (11): 1317–1324. doi:10.1124/dmd.104.000786. PMID 15282211.
- ↑ Walden J, von Wegerer J, Winter U, Berger M, Grunze H. "Effects of kawain and dihydromethysticin on field potential changes in the hippocampus.". Progress in Neuro-psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry. PMID 9194150.
See also
| |||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.