Dihydrogossypetin
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Dihydrogossypetin | |
|---|---|
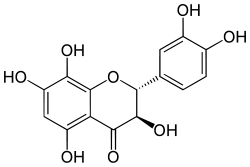 | |
| IUPAC name (2R,3R)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7,8-tetrahydroxy-2,3-dihydrochromen-4-one | |
| Other names 2,3-Dihydrogossypetin | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 489-35-0 |
| PubChem | 5460097 |
| ChemSpider | 4573761 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:16965 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:C1=CC(=C(C=C1C2C(C(=O)C3=C(O2)C(=C(C=C3O)O)O)O)O)OC1=CC(=C(C=C1[C@@H]2C(C(=O)C3=C(O2)C(=C(C=C3O)O)O)O)O)O|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C15H12O8 |
| Molar mass | 320.25 g/mol |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Dihydrogossypetin is a flavanonol, a type of flavonoid.
Metabolism
The enzyme Taxifolin 8-monooxygenase uses taxifolin, NADH, NADPH, H+, and O2 to produce 2,3-dihydrogossypetin, NAD+, NADP+, and H2O.
| |||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.