Deutscher Olympischer Sportbund
 Deutscher Olympischer Sportbund logo | |
| National Olympic Committee | |
|---|---|
| Country/Region |
|
| Code | GER |
| Created | 1895 |
| Recognized | 1895 |
| Continental Association | EOC |
| Headquarters | Frankfurt am Main, Germany |
| President | Alfons Hörmann |
| Website | http://www.dosb.de |
Deutscher Olympischer Sportbund (DOSB, German Olympic Sports Confederation) was founded on 20 May 2006 by a merger of the Deutscher Sportbund (DSB), and the Nationales Olympisches Komitee für Deutschland (NOK) which dates back to 1895, the year it was founded and recognized as NOC by the IOC.
Seated in Frankfurt am Main (like the German Football Association), it represents 89,000 clubs and 27,000,000 members, about a third of the population of Germany.
Board
DOSB-President is Alfons Hörmann. Also members of the executive board are:[1]
- Hans-Peter Krämer (Vice President, economy and finances)
- Christa Thiel (Vice President, competitive sports)
- Walter Schneeloch (Vice President, popular sports and development of sports)
- Gudrun Doll-Tepper (Vice President, education and olympic breeding)
- Ilse Ridder-Melchers (Vice President, women and equality)
- Ingo-Rolf Weiss (chairman of Deutsche Sportjugend)
- Christian Breuer (representative of the athletes)
- Michael Vesper (General Director)
- Claudia Bokel (German IOC Member)
- Thomas Bach (IOC President)
History and structure
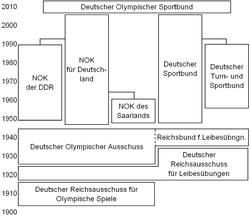

As one of the first nations, Germany founded a NOC in 1895, purposefully named "Komitee für die Beteiligung Deutschlands an den Olympischen Spielen zu Athen" ("Committee for the participation of Germany at the Olympic Games in Athens"). It was recognized by the IOC, and Germany took part in 1896 for the first time. The name of the temporary NOC changed to reflect the next two host towns, before it became permanent after 1904.
The 1916 Summer Olympics had been awarded to Berlin, but were canceled because of the duration of World War I, with Germany and other Central Powers getting excluded from the "Olympic family" which was dominated by the Entente Powers. Thus, in 1917, the "Deutscher Reichsausschuss für Olympische Spiele" (DRA, DRAfOS "German Imperial Commission for Olympic Games") was renamed Deutscher Reichsausschuss für Leibesübungen (DRL, "German Imperial Commission for Physical Exercise") to reflect and protest the non-Olympic situation.
In lieu of the Olympic Games of 1920, for which Germany and its allies were not invited, "Deutsche Kampfspiele" ("German Sports Contests") were organized, both for Summer and Winter, with the 1922 Winter edition predating the first Olympic Winter Games by two years. Hardly surprising, Berlin, having been prepared for 1916, was the site for the first Summer event:
- 1922
- Garmisch und Partenkirchen (Oberbayern)
- 18. - ??. Juni 1922 Berlin
- 1926
- Triberg und Titisee (Schwarzwald)
- 4. - 11. Juli 1926 Köln
- 1930
- Krummhübel (Riesengebirge)
- 26. - 29. Juni 1930 Breslau
Unlike others, Germany was still not invited for 1924. In 1925, the DRL split up, to remain focused on sports in Germany, while the NOC section became the Deutscher Olympischer Ausschuss (DOA, "German Olympic Commission") in order to focus on international relations and the promotion of the return of Germany to Olympics. This succeeded for 1928, with Germany taking part in both games.
The organisations remained separate, even though Nazi Germany took influence from 1933 onwards. In 1931, the IOC had decided to give both 1936 Olympic Games to Germany.
After the war, Germany was occupied and partitioned. In 1946, the DOA was dissolved. Soon, in June 1947, Adolf Friedrich zu Mecklenburg founded a new provisional Deutscher Olympischer Ausschuss, which was not recognized by IOC as it did not represent any recognized state yet. On 23 May 1949, the Federal Republic of Germany was established on the territory of the Western occupied zones. On 24 September 1949 the Nationales Olympisches Komitee für Deutschland ("National Olympic Committee for Germany") was founded in Bonn as successor to the DOA.
In October 1949, under Soviet occupation, the German Democratic Republic was founded, which on 22 April 1951 founded a separate Nationales Olympisches Komitee für Ostdeutschland ("National Olympic Committee for East Germany"), in 1965 renamed to "Nationales Olympisches Komitee der DDR" ("National Olympic Committee of the GDR"). Only in 1968 it was recognized by IOC as fully independent member.
As a third German state, under French occupation, was the Saar (protectorate) (1947–1956), which also founded sporting organisations in order to take part in international competition, like football and the Olympics. The Nationales Olympisches Komitee des Saarlandes ("National Olympic Committee") was founded in 1950 and recognized by the IOC.
After criticism due to lack of success in 2004, the Deutscher Sportbund ("German ") (DSB) and the Nationales Olympisches Komitee für Deutschland (NOK) decided to merge in 2005.
Member organisations
16 State-level member organisations
- Bayerischer Landes-Sportverband
- Hamburger Sportbund
- Landessportverband Baden-Württemberg
- Landessportbund Berlin
- Landessportbund Brandenburg
- Landessportbund Bremen
- Landessportverband für das Saarland
- Landessportbund Hessen
- Landessportbund Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
- Landessportbund Niedersachsen
- Landessportbund Nordrhein-Westfalen
- Landessportbund Rheinland-Pfalz
- Landessportbund Sachsen
- Landessportbund Sachsen-Anhalt
- Landessportverband Schleswig-Holstein
- Landessportbund Thüringen
60 member organisations
(34 Olympic sports marked with *, and 27 Non-Olympic sports)
- American Football Verband Deutschland
- Bob- und Schlittenverband für Deutschland*
- Bund Deutscher Radfahrer*
- Bundesverband Deutscher Gewichtheber*
- Bundesverband Deutscher Kraftdreikämpfer
- Deutsche Billard-Union
- Deutsche Eislauf-Union*
- Deutsche Eisschnellauf-Gemeinschaft*
- Deutsche Lebens-Rettungs-Gesellschaft
- Deutsche Reiterliche Vereinigung*
- Deutsche Taekwondo Union
- Deutsche Triathlon-Union*
- Deutscher Aero Club
- Deutscher Alpenverein
- Deutscher Athletenbund
- Deutscher Badminton-Verband*
- Deutscher Baseball und Softball Verband
- Deutscher Basketball Bund*
- Deutscher Behinderten-Sportverband
- Deutscher Boccia-, Boule- und Pétanque-Verband
- Deutscher Boxsport-Verband*
- Deutscher Curling Verband*
- Deutscher Eishockey-Bund*
- Deutscher Eisstock-Verband*
- Deutscher Fechter-Bund*
- Deutscher Fußball-Bund*
- Deutscher Gehörlosen-Sportverband
- Deutscher Golf-Verband
- Deutscher Handball-Bund*
- Deutscher Hockey Bund*
- Deutscher Ju-Jutsu Verband
- Deutscher Judobund*
- Deutscher Kanu-Verband*
- Deutscher Karate Verband*
- Deutscher Keglerbund*
- Deutscher Leichtathletik-Verband*
- Deutscher Minigolfsport Verband
- Deutscher Motor Sport Bund
- Deutscher Motorsport Verband
- Deutscher Motoryachtverband
- Deutscher Rasenkraftsport- und Tauzieh-Verband
- Deutscher Ringer-Bund*
- Deutscher Rollsport und Inline-Verband
- Deutscher Ruderverband*
- Deutscher Rugby-Verband*
- Deutscher Schachbund
- Deutscher Schwimm-Verband*
- Deutscher Schützenbund*
- Deutscher Segler-Verband*
- Deutscher Skibob-Verband
- Deutscher Skiverband*
- Deutscher Sportakrobatik-Bund
- Deutscher Squash und Rackets Verband
- Deutscher Tanzsportverband
- Deutscher Tennis Bund*
- Deutscher Tischtennis-Bund*
- Deutscher Turner-Bund*
- Deutscher Verband für Modernen Fünfkampf*
- Deutscher Volleyball-Verband*
- Deutscher Wasserski-Verband
- Verband Deutscher Sportfischer
- Verband Deutscher Sporttaucher
19 specials member organisations
- Allgemeiner Deutscher Hochschulsportverband
- Bundesverband staatlich anerkannter Berufsfachschulen für Gymnastik und Sport
- CVJM-Gesamtverband in Deutschland – CVJM-Sport-
- Deutsche Gesellschaft für Sportmedizin und Prävention
- Deutsche Olympische Gesellschaft
- Deutsche Vereinigung für Sportwissenschaft
- Deutscher Aikido-Bund
- Deutscher Betriebssportverband
- Deutscher Sportlehrerverband
- Deutscher Verband für Freikörperkultur (DFK)
- Deutscher Verband für das Skilehrwesen- Interski Deutschland
- Deutsches Polizeisportkuratorium
- Deutsche Jugendkraft|DJK-Sportverband
- Gewerkschaft Erziehung und Wissenschaft - Sportkommission
- Kneipp-Bund
- Makkabi Deutschland
- Rad- und Kraftfahrerbund (RKB) "Solidarität" Deutschland 1896
- Stiftung Sicherheit im Skisport
- Verband Deutscher Eisenbahner-Sportvereine