Desargues graph
| Desargues graph | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Named after | Gérard Desargues |
| Vertices | 20 |
| Edges | 30 |
| Radius | 5 |
| Diameter | 5 |
| Girth | 6 |
| Automorphisms | 240 (S5× Z/2Z) |
| Chromatic number | 2 |
| Chromatic index | 3 |
| Genus | 2 |
| Properties |
Cubic Distance-regular Hamiltonian Bipartite Symmetric |
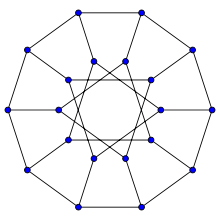
In the mathematical field of graph theory, the Desargues graph is a distance-transitive cubic graph with 20 vertices and 30 edges.[1] It is named after Gérard Desargues, arises from several different combinatorial constructions, has a high level of symmetry, is the only known non-planar cubic partial cube, and has been applied in chemical databases.
The name "Desargues graph" has also been used to refer to a ten-vertex graph, the complement of the Petersen graph, which can also be formed as the bipartite half of the 20-vertex Desargues graph.[2]
Constructions
There are several different ways of constructing the Desargues graph:
- It is the generalized Petersen graph G(10, 3). To form the Desargues graph in this way, connect ten of the vertices into a regular decagon, and connect the other ten vertices into a ten-pointed star that connects pairs of vertices at distance three in a second decagon. The Desargue graph consists of the 20 edges of these two polygons together with an additional 10 edges connecting points of one decagon to the corresponding points of the other.
- It is the Levi graph of the Desargues configuration. This configuration consists of ten points and ten lines describing two perspective triangles, their center of perspectivity, and their axis of perspectivity. The Desargues graph has one vertex for each point, one vertex for each line, and one edge for every incident point-line pair. Desargues' theorem, named after 17th-century French mathematician Gérard Desargues, describes a set of points and lines forming this configuration, and the configuration and the graph take their name from it.
- It is the bipartite double cover of the Petersen graph, formed by replacing each Petersen graph vertex by a pair of vertices and each Petersen graph edge by a pair of crossed edges.
- It is the bipartite Kneser graph H5,2. Its vertices can be labeled by the ten two-element subsets and the ten three-element subsets of a five-element set, with an edge connecting two vertices when one of the corresponding sets is a subset of the other.
- The Desargues graph is Hamiltonian and can be constructed from the LCF notation: [5,−5,9,−9]5.
Algebraic properties
The Desargues graph is a symmetric graph: it has symmetries that take any vertex to any other vertex and any edge to any other edge. Its symmetry group has order 240, and is isomorphic to the product of a symmetric group on 5 points with a group of order 2.
One can interpret this product representation of the symmetry group in terms of the constructions of the Desargues graph: the symmetric group on five points is the symmetry group of the Desargues configuration, and the order-2 subgroup swaps the roles of the vertices that represent points of the Desargues configuration and the vertices that represent lines. Alternatively, in terms of the bipartite Kneser graph, the symmetric group on five points acts separately on the two-element and three-element subsets of the five points, and complementation of subsets forms a group of order two that transforms one type of subset into the other. The symmetric group on five points is also the symmetry group of the Petersen graph, and the order-2 subgroup swaps the vertices within each pair of vertices formed in the double cover construction.
The generalized Petersen graph G(n, k) is vertex-transitive if and only if n = 10 and k = 2 or if k2 ≡ ±1 (mod n) and is edge-transitive only in the following seven cases: (n, k) = (4, 1), (5, 2), (8, 3), (10, 2), (10, 3), (12, 5), (24, 5).[3] So the Desargues graph is one of only seven symmetric Generalized Petersen graphs. Among these seven graphs are the cubical graph G(4, 1), the Petersen graph G(5, 2), the Möbius–Kantor graph G(8, 3), the dodecahedral graph G(10, 2) and the Nauru graph G(12, 5).
The characteristic polynomial of the Desargues graph is
Therefore the Desargues graph is an integral graph: its spectrum consists entirely of integers.
Applications
In chemistry, the Desargues graph is known as the Desargues–Levi graph; it is used to organize systems of stereoisomers of 5-ligand compounds. In this application, the thirty edges of the graph correspond to pseudorotations of the ligands.[4][5]
Other properties
The Desargues graph has rectilinear crossing number 6, and is the smallest cubic graph with that crossing number (sequence A110507 in OEIS). It is the only known nonplanar cubic partial cube.[6]
The Desargues graph has chromatic number 2, chromatic index 3, radius 5, diameter 5 and girth 6. It is also a 3-vertex-connected and a 3-edge-connected Hamiltonian graph.
All the cubic distance-regular graphs are known.[7] The Desargues graph is one of the 13 such graphs.
Gallery
-

Desargues graph colored to highlight various cycles.
-

The chromatic index of the Desargues graph is 3.
-
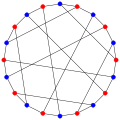
The chromatic number of the Desargues graph is 2.
References
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W., "Desargues Graph", MathWorld.
- ↑ Kagno, I. N. (1947), "Desargues' and Pappus' graphs and their groups", American Journal of Mathematics (The Johns Hopkins University Press) 69 (4): 859–863, doi:10.2307/2371806, JSTOR 2371806.
- ↑ Frucht, R.; Graver, J. E.; Watkins, M. E. (1971), "The groups of the generalized Petersen graphs", Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society 70 (02): 211–218, doi:10.1017/S0305004100049811.
- ↑ Balaban, A. T.; Fǎrcaşiu, D.; Bǎnicǎ, R. (1966), "Graphs of multiple 1, 2-shifts in carbonium ions and related systems", Rev. Roum. Chim. 11: 1205
- ↑ Mislow, Kurt (1970), "Role of pseudorotation in the stereochemistry of nucleophilic displacement reactions", Acc. Chem. Res. 3 (10): 321–331, doi:10.1021/ar50034a001
- ↑ Klavžar, Sandi; Lipovec, Alenka (2003), "Partial cubes as subdivision graphs and as generalized Petersen graphs", Discrete Mathematics 263: 157–165, doi:10.1016/S0012-365X(02)00575-7
- ↑ Brouwer, A. E.; Cohen, A. M.; and Neumaier, A. Distance-Regular Graphs. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1989.
