Dühring's rule
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
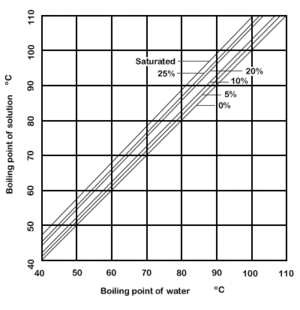
Dühring's rule states that a linear relationship exists between the temperatures at which two solutions exert the same vapor pressure.[1][2] The rule is often used to compare a pure liquid and a solution at a given concentration.
Dühring's plot is a graphical representation of such a relationship, typically with the pure liquid's boiling point along the x-axis and the mixture's boiling point along the y-axis; each line of the graph represents a constant concentration.
See also
- Solubility
- Evaporator
- Raoult's Law
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Earle, Richard L.; Earle, M. D. (2004). "Evaporation". Unit Operations in Food Processing. The New Zealand Institute of Food Science & Technology (Inc.). Retrieved March 15, 2009.
- ↑ Price, R. M. (2003). "Evaporation". RMP Lecture Notes. Christian Brothers University. Retrieved March 15, 2009.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.