Cytochalasin E
| Cytochalasin E[1] | |
|---|---|
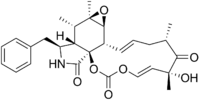 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 36011-19-5 |
| PubChem | 5458385 |
| ChemSpider | 4572350 |
| EC number | 252-835-7 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:C[C@H]1C/C=C/[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@](O3)([C@H]([C@@H]4[C@]2(C(=O)N[C@H]4CC5=CC=CC=C5)OC(=O)O/C=C/[C@@](C1=O)(C)O)C)C|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C28H33NO7 |
| Molar mass | 495.56 g mol−1 |
| Density | 1.309 g/ml |
| Hazards | |
| EU classification | T+ |
| R-phrases | R26/27/28 R63 |
| S-phrases | S28 S36/37 S45 |
| Main hazards | Toxic |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Cytochalasin E, a member of the cytochalasin group, is an inhibitor of actin polymerization in blood platelets. It inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth. Unlike cytochalasin A and cytochalasin B, it does not inhibit glucose transport.
Because of its antiangiogenic effect, cytochalasin E is a potential drug for age-related macular degeneration, a kind of blindness caused by an abnormal proliferation of blood vessels in the eye.[2]
References
External pages
Cytochalasin E from Fermentek
Cytochalasin E from Cayman Chemical